Learn Something New
Questions I asked A.I.
learnsomethingnew.carrd.co
An “otrovert” is a newly defined personality type describing people who enjoy socializing but feel like outsiders in groups, preferring one-on-one connections over belonging to a crowd.---## 🌟 What It Means to Be an Otrovert
- Coined by Dr. Rami Kaminski (American psychiatrist) in 2023, the term describes individuals who don’t fit neatly into introvert, extrovert, or ambivert categories.
- Core trait: Otroverts are sociable and popular, but they don’t feel a strong sense of belonging in groups. Instead, they thrive in one-on-one relationships.
- Outsiders treated like insiders: They’re welcomed into social settings but often feel like they don’t fully fit in.
- Energy source: Unlike introverts (energized by solitude) or extroverts (energized by crowds), otroverts don’t rely on inward or outward focus for energy. Their personality is shaped more by social environment and context.---## 🔎 Comparison With Other Personality Types| Personality Type | Key Traits | Social Preference | Sense of Belonging |
|------------------|------------|------------------|--------------------|
| Introvert | Reflective, reserved, energized by solitude | Prefers small groups or alone time | Stronger identity in solitude |
| Extrovert | Outgoing, expressive, energized by crowds | Loves large groups, parties | Feels belonging in groups |
| Ambivert | Balanced mix of introvert & extrovert traits | Comfortable in both settings | Flexible sense of belonging |
| Otrovert | Sociable but feels like an outsider | Prefers one-on-one interactions | Welcomed but doesn’t feel they fit in |Sources:---## 🧩 Signs You Might Be an Otrovert
- You enjoy meeting people individually but dislike group dynamics.
- You’re often included socially yet feel like you don’t truly belong.
- You prefer to observe rather than actively participate in group settings.
- You value deep, personal connections over popularity or group identity.---## 💡 Why This Term Matters
The rise of “otrovert” reflects a growing recognition that personality isn’t binary. Many people don’t fit neatly into introvert or extrovert categories, and this new label helps explain the nuanced middle ground. It validates those who feel socially engaged but not group-oriented, offering language to better understand themselves and their relationships.
Quick Answer: Some supplements that have been studied for ADHD include omega-3 fatty acids, zinc, iron, magnesium, vitamin D, melatonin, and certain amino acids like L-theanine. Evidence is mixed, and they are not replacements for medication or therapy, but they may help manage specific symptoms when deficiencies are present.---## 🌿 Commonly Studied Supplements for ADHD| Supplement | Potential Benefit | Notes |
|------------|------------------|-------|
| Omega-3 fatty acids (EPA/DHA) | May improve attention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity | Found in fish oil; mixed evidence but often recommended |
| Zinc | Supports dopamine regulation; may reduce hyperactivity/impulsivity | Deficiency more common in ADHD; excess zinc can be harmful |
| Iron (ferritin levels) | Important for brain function and dopamine synthesis | Low iron linked to ADHD; supplementation only if deficient |
| Magnesium | May help with relaxation, sleep, and rebound effects after stimulant meds | Often combined with vitamin D in studies |
| Vitamin D | Low levels associated with ADHD; may improve attention | Supplementation helpful if deficient |
| Melatonin | Improves sleep onset and duration | Does not treat ADHD directly, but helps with sleep issues |
| L-theanine | May improve attention and inhibitory control | Limited but promising evidence, often paired with caffeine |
| B vitamins (B6, B9, B12) | Linked to neurotransmitter function | Some studies show low levels in ADHD |
| Probiotics | Gut health may influence cognition and mood | Early research suggests possible benefit |
| Herbal options (ginseng, ginkgo, St. John’s wort) | Studied for cognitive support | Evidence limited; may interact with medications |Sources: Healthline’s overview of ADHD supplements, ADDitude’s integrative treatment guide, Verywell Health’s review of natural ADHD supplements---## ⚖️ Key Takeaways- Evidence is mixed: Supplements may help if there’s a deficiency, but they are not proven standalone treatments.
- Best supported: Omega-3s, zinc, iron, magnesium, vitamin D, and melatonin have the most consistent research.
- Safety first: Always check nutrient levels (like iron or vitamin D) before supplementing, since excess can be harmful.
- Complementary role: Supplements are best used alongside ADHD medication, behavioral therapy, and lifestyle strategies.---
Quick Answer: Creatine is being studied for its potential cognitive benefits, but evidence that it directly helps ADHD symptoms is limited and mixed. It may support brain energy metabolism, yet it is not an established ADHD treatment. Always consult a healthcare professional before considering it.---## 🧠 What Research Suggests- Creatine’s role in the brain: Creatine helps regenerate ATP, the brain’s energy currency. Since ADHD has been linked to possible energy metabolism challenges in the prefrontal cortex, creatine supplementation could theoretically support attention and executive function.
- Preliminary findings: Some studies suggest creatine may improve working memory, attention span, and processing speed, especially in adults or individuals with medical conditions.
- Mixed results: Other research shows no significant improvements in ADHD-specific symptoms or executive function after creatine use.
- Community experiences: Anecdotal reports vary—some people say creatine improves focus and mental energy, while others feel it worsens hyperactivity or racing thoughts.---## ⚖️ Pros and Cons of Creatine for ADHD| Potential Benefits | Possible Concerns |
|--------------------|-------------------|
| Supports brain energy metabolism | Limited direct evidence for ADHD symptom relief |
| May improve memory and processing speed | Some users report worsened hyperactivity or focus issues |
| Generally safe at recommended doses | Can cause water retention, digestive discomfort |
| Widely studied for physical performance | Unknown long-term effects when combined with ADHD meds |Sources:---## 🔍 Safety and Interactions- Safety profile: Creatine is considered safe for healthy individuals at typical doses (3–5 g/day).
- Medication interactions: Formal studies on creatine with ADHD stimulants (like Adderall or Ritalin) are scarce. Both can affect cardiovascular function, so combining them may theoretically increase heart rate or blood pressure.
- Withdrawal effects: Some anecdotal reports suggest stopping creatine suddenly may lower dopamine levels, which could affect mood in people with ADHD.---## ✅ TakeawayCreatine is not a proven ADHD treatment, but it may offer indirect cognitive benefits by supporting brain energy. If you’re curious about trying it, the safest path is to discuss it with your doctor, especially if you’re on ADHD medication or have other health conditions.
Quick Answer: To gatekeep something means to control or restrict access to it—whether that’s information, resources, opportunities, or even cultural trends. It often implies deciding who gets “in” and who doesn’t.---### 🔑 Core Meaning
- General Definition: Gatekeeping is the act of controlling who has access to something, such as knowledge, resources, or opportunities.
- Sociological Roots: The term comes from sociology, where gatekeepers decide what information or opportunities flow to others.
- Modern Usage: Online, it’s often used critically to describe people who withhold knowledge or resources to maintain exclusivity.---### 📱 In Everyday & Online Contexts
- Communities & Fandoms: Someone might “gatekeep” by saying only true fans of a band know certain songs, excluding newcomers.
- Social Media: Phrases like “not trying to gatekeep” are used when someone shares a tip, product, or hack that they could have kept secret.
- Playful Use: Sometimes it’s joking—like pretending to keep a favorite restaurant or brand “exclusive.”
- Negative Connotation: More often, it’s seen as elitist or exclusionary, discouraging inclusivity.---### ⚖️ Positive vs. Negative
| Context | Positive Gatekeeping | Negative Gatekeeping |
|-------------|--------------------------|--------------------------|
| Group settings | A facilitator ensures no one dominates discussion | Someone blocks others from joining or learning |
| Online communities | Protecting safe spaces from trolls | Withholding info to feel superior |
| Culture/trends | Preserving authenticity | Excluding newcomers from enjoying it |Sources:---👉 In short, to gatekeep means deciding who gets access and who doesn’t. Sometimes it’s necessary (like moderating a group), but often it’s criticized when used to hoard knowledge or exclude others.
Quick Answer: Yes, clearing your phone’s cache can be beneficial if done occasionally, especially when your device feels sluggish or storage is tight. It frees up space, improves performance, and protects privacy—but doing it too often may slow apps temporarily as they rebuild their cache.---## 📱 What Cache Is
- Cache is temporary data stored by apps and browsers to speed up loading and improve user experience.
- Examples: images from websites, app data, or temporary files that prevent repeated downloads.---## ✅ Benefits of Clearing Cache
- Frees up storage space: Cached files can accumulate and take up gigabytes over time.
- Improves performance: Removing bloated or outdated cache can reduce lag and app crashes.
- Enhances privacy: Clearing browser cache and history helps protect personal data from unwanted access.
- Fixes glitches: Sometimes corrupted cache causes apps to misbehave; clearing it resets them.---## ⚠️ Downsides of Clearing Cache Too Often
- Temporary slowdowns: Apps may load slower initially as they rebuild cache.
- Loss of convenience: Cached data (like saved images or login sessions) may need to be reloaded.
- Not always necessary: Modern phones manage cache efficiently; frequent clearing isn’t required unless issues arise.---## 📊 Comparison Table| Aspect | Clearing Cache Regularly | Keeping Cache |
|------------------------|--------------------------|---------------|
| Storage Space | Frees up space | Can become bloated |
| Performance | Boosts speed if sluggish | Usually smooth unless overloaded |
| Privacy | Safer, less traceable | More personal data stored |
| App Responsiveness | May slow briefly after clearing | Faster with cached data |
| Best Use Case | When phone lags or storage is low | Everyday use without issues |Sources:---## 🧭 Practical Recommendation
- Do it occasionally, not daily.
- Clear cache when:
- Your phone feels slow.
- Storage space is running low.
- You want to remove browsing traces for privacy.
- For routine maintenance, once every few weeks or months is usually enough.
A venture capitalist (VC) is an investor who provides funding to early-stage or high-growth companies in exchange for equity (ownership) in the business. They take on significant risk by backing startups, hoping that some will grow rapidly and deliver large returns.---## 🌟 Key Points About Venture Capitalists- Definition: A venture capitalist is a type of private equity investor who supplies capital to startups or small companies with strong growth potential.
- Exchange for Equity: Instead of lending money, VCs invest in return for an ownership stake in the company.
- Funding Source: Venture capital firms pool money from wealthy individuals, pension funds, insurance companies, and other institutions.
- Risk & Reward: Startups are risky—many fail—but successful ones can deliver massive profits (think Google, Facebook, or Uber in their early days).
- Role in Innovation: Venture capital has fueled groundbreaking technologies like semiconductors, smartphones, and artificial intelligence.---## 📊 Venture Capitalist vs Other Investors| Investor Type | What They Provide | Typical Stage of Investment | Risk Level | Expected Return |
|------------------------|------------------|-----------------------------|------------|----------------|
| Venture Capitalist | Equity funding | Early-stage startups | High | Very high (if successful) |
| Angel Investor | Personal funds | Very early (idea stage) | High | High |
| Private Equity Firm| Large capital | Mature companies | Moderate | Moderate |
| Bank/Lender | Loans (debt) | Any stage, but requires collateral | Low | Fixed interest |Sources:---## 🚀 Why Venture Capitalists Matter
- They bridge the gap between entrepreneurs with big ideas and the resources needed to scale.
- They often provide mentorship, networking, and strategic guidance alongside money.
- Without venture capital, many iconic companies might never have grown beyond the garage or dorm room where they started.
Short Answer: Yes, creatine can make kidney tests look “wrong” even if your kidneys are fine, because the test measures creatinine (a waste product made when your body uses creatine), and taking extra creatine can raise that number without real kidney damage.---### 🧒 Explaining Like You’re 10Imagine your body is like a busy kitchen:
- Creatine is like flour you use to bake bread (your muscles use it for energy).
- When you bake, you end up with crumbs. Those crumbs are called creatinine.
- Your kidneys are like the clean-up crew that sweeps the crumbs out.Now, doctors check how many crumbs (creatinine) are lying around in the kitchen to see if the clean-up crew (your kidneys) is doing its job.👉 But here’s the trick: if you dump extra flour (creatine supplements) into the kitchen, you’ll naturally make more crumbs. So when the doctor looks, they might think the clean-up crew is slacking off—when really, you just had more flour to begin with.---### ⚡ Why This Happens
- Creatine turns into creatinine when your muscles use it.
- Kidney tests measure creatinine, not creatine directly.
- Extra creatine → extra creatinine → test looks “bad.”
- But your kidneys may still be perfectly healthy.---### 🧾 Key Points
- Creatine itself doesn’t hurt healthy kidneys.
- It can raise creatinine levels, which is the number doctors use to check kidney health.
- That’s why doctors sometimes ask people to stop creatine before a kidney test, so the results aren’t misleading.---So, in kid terms: Creatine makes more crumbs, and the test only sees crumbs. That can trick the doctor into thinking your kidneys are messy when they’re actually fine.Sources:---
Quick Answer: The most fuel-efficient highway speed for most vehicles is typically between 40–55 mph, with fuel economy dropping noticeably once you go above 60 mph.---## 🚗 Why Speed Matters for Gas Mileage
- Aerodynamic drag: Resistance from the air increases exponentially with speed. At 70–75 mph, your car is pushing through much more air than at 55 mph, which burns more fuel.
- Engine efficiency curve: Most engines are tuned to deliver peak efficiency at moderate speeds, not at high RPMs.
- Vehicle type: Smaller, lighter, aerodynamic cars can maintain efficiency at slightly higher speeds, while heavier vehicles (SUVs, trucks) lose efficiency sooner.---## ⚖️ Comparison Table: Speed vs. Fuel Efficiency| Speed (mph) | Fuel Efficiency Trend | Notes |
|-------------|-----------------------|-------|
| 35–40 | Very high efficiency | Often impractical on highways; best for rural roads |
| 45–55 | Optimal range | Sweet spot for most cars; balances time and MPG |
| 60 | Efficiency begins to drop | Still decent, but drag increases |
| 65–75 | Noticeable decline | Faster travel, but costs more fuel |
| 80+ | Very inefficient | High drag, high RPM, steep MPG loss |Sources:---## 🛠️ Practical Tips
- Cruise control: Helps maintain steady speed, reducing unnecessary acceleration.
- Avoid rapid acceleration/braking: Smooth driving conserves fuel.
- Check tire pressure: Underinflated tires increase rolling resistance.
- Lighten the load: Extra cargo weight reduces efficiency.---## 🎯 Bottom Line
If your goal is maximum gas mileage, aim for 45–55 mph on the highway. If your goal is time savings, driving faster may shave minutes off but at the cost of significantly higher fuel consumption.
A “screed” can mean either a long, tedious piece of writing or a construction tool/layer used in building.Here’s the breakdown:### 📖 Literary Meaning
- Lengthy discourse or rant: A screed often refers to a long, monotonous, or ranting piece of writing, such as a diatribe or manifesto.
- Informal writing: It can also mean an informal letter or essay, especially one that feels excessive or overly opinionated.
- Example: “She published a screed against the recording industry,” meaning a long, angry essay.### 🏗️ Construction Meaning
- Leveling strip or layer: In building trades, a screed is a strip of plaster, wood, or metal applied to a surface to guide the even application of plaster or concrete.
- Tool for smoothing: It can also refer to the flat board or tool used to smooth freshly poured concrete.
- Final surface layer: In flooring, a screed may mean the thin, top layer of concrete or cement laid to create a level surface.### ⚡ Quick Comparison| Context | Meaning of Screed |
|----------------|-------------------|
| Writing | Long, tedious, ranting piece of text |
| Construction | Tool, strip, or layer used to level plaster/concrete |So, depending on whether you’re talking about words or walls/floors, “screed” can mean either a rant or a leveling layer/tool.
For a family of five in the U.S. in 2025, the average monthly grocery budget is around $1,600–$1,800, while total living expenses (food, clothing, personal care, housekeeping, miscellaneous) typically range from $2,500–$2,600 per month.**---### 🛒 Grocery Costs
- Per person grocery average: About $363 per month for adults.
- Family of 5 estimate: Roughly $1,815 per month (5 × $363).
- National survey data: Many households report spending $235 per week per person, which equals $940–$1,175 per week for a family of 5, or $3,800–$4,700 per month depending on habits.
- SoFi guidance: Families of five should expect $1,000–$1,600 per month depending on diet, location, and shopping style.### 🏠 Living Expenses (IRS National Standards, 2025)
The IRS publishes “Allowable Living Expenses” as a benchmark for household budgets:| Category | 4-person household | Add per extra person | Family of 5 total |
|----------|-------------------|----------------------|-------------------|
| Food | $1,255 | +$394 | $1,649 |
| Housekeeping supplies | $91 | +$16 | $107 |
| Apparel & services | $276 | +$88 | $364 |
| Personal care | $117 | +$23 | $140 |
| Miscellaneous | $390 | +$77 | $467 |
| Total | $2,129 | +$598 | $2,727 |So, the IRS benchmark suggests $2,700+ per month for basic living expenses for a family of five.### ⚖️ Key Takeaways
- Groceries alone: Expect $1,600–$1,800 per month as a baseline, though higher if eating out or buying premium items.
- Full living expenses: Around $2,500–$2,700 per month, excluding housing, transportation, healthcare, and savings.
- Variation factors: Location (urban vs. rural), dietary choices (organic, specialty diets), and shopping habits (bulk buying, meal prep).
Festivus is celebrated every year on December 23. It’s a quirky, secular holiday created as an alternative to the pressures and commercialism of Christmas, made famous by the TV show Seinfeld.---### 🎉 What Festivus Is
- Origin: Festivus was originally invented by author Daniel O’Keefe in the 1960s. His son, Dan O’Keefe, later wrote it into the Seinfeld episode The Strike (aired in 1997), which propelled it into pop culture.
- Purpose: It’s meant to be a humorous, non-commercial holiday for “the rest of us,” poking fun at traditional holiday stress and consumerism.
- Type: A secular holiday, not tied to religion, but embraced by fans of Seinfeld and those who enjoy offbeat traditions.---### 🏆 Traditions of Festivus
Festivus celebrations include several unique rituals:
- The Festivus Pole: Instead of a decorated tree, participants display a plain aluminum pole with no ornaments.
- Airing of Grievances: During the Festivus dinner, everyone shares how others have disappointed them over the past year.
- Feats of Strength: After dinner, the head of the household challenges someone to a wrestling match, and Festivus isn’t over until the challenger is pinned.
- Festivus Miracles: Everyday, mundane events are humorously declared “miracles”.---### 📅 When It Happens
- Date: Always on December 23, just before Christmas.
- Frequency: Annual, celebrated by fans and communities worldwide.---### 🌍 Why People Celebrate
- Some enjoy it as a parody of holiday traditions.
- Others embrace it as a genuine alternative to Christmas stress.
- It’s become a pop culture phenomenon, with Festivus parties, social media posts, and even public displays of Festivus poles in some towns.---So, Festivus is both a joke and a real celebration—an anti-holiday holiday that’s grown beyond Seinfeld into a fun tradition for anyone who wants to skip the tinsel and embrace something offbeat.
An em dash (—) is a long punctuation mark used to create emphasis, show interruptions, or replace commas, parentheses, or colons in a sentence. It’s named “em” because its length is roughly the width of the letter M.---### ✨ Key Facts About Em Dashes
- Shape & Size: The em dash (—) is longer than the en dash (–) and the hyphen (-).
- Uses:
- To set off extra information: She finally arrived—three hours late—to the surprise of everyone.
- To replace parentheses: The car—an old, rusty sedan—barely made it up the hill.
- To replace a colon: He had only one goal—victory.
- To show interruptions or sudden breaks: “Wait—did you hear that?”
- Tone: Em dashes add emphasis and drama compared to commas, making writing feel more dynamic.
- Limitations: Best used sparingly—typically no more than two per sentence—otherwise they can make text harder to follow.---### 📏 Comparison Table| Symbol | Length | Common Use |
|--------|--------|------------|
| Hyphen (-) | Short | Joins words (well-known) |
| En dash (–) | Medium | Ranges (1990–2000) |
| Em dash (—) | Long | Breaks, emphasis, interruptions |
Yes — you can microwave plain popcorn kernels in a brown paper bag without oil. It’s a simple, healthy method that works well, though you need to watch closely to avoid burning.---### 🌽 How to Do It
- Step 1: Place about ¼ cup of popcorn kernels into a clean brown paper lunch bag.
- Step 2: Fold the top of the bag over 2–3 times to keep kernels inside.
- Step 3: Microwave on high power for 2–3 minutes, stopping when popping slows to about 2 seconds between pops.
- Step 4: Carefully open the bag (steam will escape) and season as you like — salt, spices, or melted butter afterward if desired.---### ⚠️ Safety & Tips
- No oil is required. The kernels pop from their own moisture, making this essentially air-popped popcorn.
- Paper bag caution: Brown paper bags aren’t officially designed for microwave use, so keep an eye on it. Don’t leave unattended — stop early if you smell scorching.
- Yield: ¼ cup kernels makes about 2–3 cups of popped popcorn.
- Flavoring: Add seasonings after popping. If you want butter or oil, drizzle afterward rather than microwaving with it.---### ✅ Why This Works
Popcorn kernels contain a small amount of water inside. When heated, the water turns to steam, building pressure until the kernel bursts open. The paper bag simply keeps the kernels contained and allows steam to escape, mimicking an air popper.---So yes — you can absolutely make popcorn this way. It’s quick, cheap, and healthier than store-bought microwave bags.
Opaque means something that does not let light pass through, making it impossible to see through. It can also describe writing, speech, or ideas that are difficult to understand.---## 🌐 Detailed Definition
- Physical property:
- Opaque materials block the passage of radiant energy, especially light. For example, opaque glass or muddy river water prevents visibility through it.
- Figurative meaning:
- Used to describe something hard to understand, obscure, or unclear. For instance, “opaque prose” means writing that is confusing or difficult to interpret.
- Synonyms: murky, cloudy, obscure, cryptic, enigmatic, dull.
- Opposite: transparent (clear, see-through) or translucent (partially see-through).---## 📌 Examples
- Literal:
- A brick wall is opaque because no light passes through it.
- Black paint on a window makes the glass opaque.
- Figurative:
- “The professor’s explanation was opaque” → meaning it was confusing or unclear.
- “Company policies remain opaque” → meaning they are not transparent or easy to understand.---## ⚖️ Comparison Table| Term | Light Transmission | Example |
|--------------|-------------------|----------------------------------|
| Transparent | Allows all light | Clear glass window |
| Translucent | Allows partial | Frosted bathroom glass |
| Opaque | Blocks completely | Wooden door, brick wall |Sources:---So, opaque = not see-through + often hard to understand.
Tahini is a paste made from ground sesame seeds, while tahini sauce is a dressing made by mixing tahini with lemon juice, garlic, salt, and water.---### 🌱 What is Tahini?
- Definition: Tahini is a thick, oily paste made by grinding sesame seeds into a smooth butter-like consistency.
- Origin: It’s a staple in Middle Eastern, Mediterranean, and North African cuisines.
- Flavor & Texture: Nutty, slightly bitter, and creamy—similar to natural peanut butter but with a distinct sesame taste.
- Uses:
- Base ingredient in hummus and baba ghanoush
- Spread or dip on its own
- Incorporated into dressings, sauces, and desserts like cookies or halva---### 🥗 What is Tahini Sauce?
- Definition: Tahini sauce is made by blending tahini paste with lemon juice, garlic, salt, and water.
- Flavor Profile: Creamy, tangy, nutty, and slightly garlicky.
- Common Uses:
- Drizzled over falafel, shawarma, or grilled meats
- Served with pita bread and vegetables
- Used as a salad dressing or dip
- Difference from Hummus: Hummus includes chickpeas, while tahini sauce is chickpea-free—just tahini thinned and flavored.---### ⚖️ Quick Comparison| Feature | Tahini (Paste) | Tahini Sauce |
|--------------------|----------------|--------------|
| Main Ingredient | Ground sesame seeds | Tahini + lemon juice, garlic, salt, water |
| Texture | Thick, oily, peanut-butter-like | Creamy, pourable dressing |
| Flavor | Nutty, slightly bitter | Nutty, tangy, garlicky |
| Uses | Hummus, baba ghanoush, desserts | Falafel, shawarma, salads, dips |---Tahini is the base ingredient, while tahini sauce is the prepared condiment that elevates dishes with brightness and creaminess.
Carob is a Mediterranean tree (Ceratonia siliqua) that produces sweet, edible pods often used as a caffeine‑free alternative to chocolate.---### 🌱 What Carob Is
- Carob comes from the carob tree, a flowering evergreen in the legume family (Fabaceae).
- It is native to the Mediterranean and Middle East, with Spain, Italy, and Morocco being major producers.
- The tree produces dark brown pods containing pulp and hard seeds. These pods are the edible part.### 🍫 Culinary Uses
- Carob powder (made from dried, roasted pods) is commonly used as a chocolate substitute. Unlike cocoa, it is naturally sweet and contains no caffeine.
- Carob can be found as powder, chips, syrup, or gum, used in cookies, cakes, cereal bars, and even animal feed.
- Historically, people in Cyprus made a sweet syrup from carob pods, sometimes called “carob honey”.### 💪 Nutritional & Health Aspects
- Carob is high in fiber and contains antioxidants (polyphenols).
- It is low in calories and provides B vitamins, calcium, and magnesium.
- Some studies suggest carob may help with diarrhea, lowering cholesterol, and regulating blood sugar, though scientific evidence is limited.### 🌍 Fun Facts
- Carob is also known as St. John’s bread or locust bean, linked to the belief that John the Baptist survived on carob pods.
- The seeds were historically used as a weight standard for gemstones, which is where the term “carat” comes from.---👉 In short: Carob is a naturally sweet, caffeine‑free pod from the Mediterranean carob tree, often used as a healthier alternative to chocolate.
The main difference between olive oils lies in how much they’re processed, which affects flavor, quality, and best use. Extra virgin olive oil is the least processed and most flavorful, while refined and blended varieties are milder and better for high-heat cooking.---## 🌿 Key Types of Olive Oil### 1. Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO)
- Highest quality, least processed: Made by mechanically pressing olives without heat or chemicals.
- Flavor: Fruity, peppery, and robust; closest to the taste of fresh olives.
- Best use: Raw applications—salads, drizzling, dips, finishing dishes.
- Health benefits: Rich in antioxidants and polyphenols.### 2. Virgin Olive Oil
- Similar to EVOO but slightly lower quality: Still mechanically extracted, but may have minor flavor defects.
- Flavor: Less intense than EVOO, but still retains olive character.
- Best use: Everyday cooking where strong flavor isn’t essential.### 3. Refined Olive Oil
- Highly processed: Made by refining lower-quality oils with heat or chemicals.
- Flavor: Neutral, lacking the fruity notes of virgin oils.
- Best use: Frying, sautéing, or recipes where you don’t want olive flavor to dominate.### 4. Classic / Pure Olive Oil
- Blend of refined + virgin/EVOO: Offers a balance of mild flavor and affordability.
- Flavor: Softer than EVOO, with some olive notes.
- Best use: General cooking, roasting, or baking.### 5. Light or Mild Olive Oil
- Marketing term, not fewer calories: Refers to lighter flavor, achieved by refining.
- Flavor: Very subtle, almost neutral.
- Best use: Baking, frying, or dishes where you don’t want olive taste.---## 🧾 Quick Comparison Table| Type | Processing Level | Flavor Profile | Best Use |
|-----------------------|------------------|----------------------|-----------------------------------|
| Extra Virgin (EVOO) | Minimal, cold-pressed | Fruity, robust, peppery | Salads, dips, finishing touches |
| Virgin | Minimal, slight defects | Mild olive flavor | Everyday cooking |
| Refined | Heat/chemical refined | Neutral | Frying, sautéing |
| Classic/Pure | Blend refined + virgin | Balanced, mild | Roasting, baking |
| Light/Mild | Refined, marketed mild | Very subtle | Baking, high-heat cooking |---## ✅ Takeaway
- Use EVOO when flavor matters (salads, dressings, finishing).
- Use refined or light olive oils for frying or baking where neutral taste is better.
- Classic blends are versatile middle-ground options.
GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) is a natural hormone made in your gut that helps regulate blood sugar and appetite. It stimulates insulin release, suppresses glucagon (which raises blood sugar), slows stomach emptying, and increases feelings of fullness. Because of these effects, GLP-1 receptor agonist medications are widely used to treat type 2 diabetes and obesity.---### 🔬 What GLP-1 Does in the Body
- Produced in the intestine after eating, especially by L-cells in the small intestine and colon.
- Triggers insulin release from the pancreas in a glucose-dependent way (only when blood sugar is high).
- Suppresses glucagon secretion, preventing excess sugar release into the bloodstream.
- Slows gastric emptying, which reduces post-meal blood sugar spikes.
- Promotes satiety, making you feel fuller and reducing appetite.---### 💊 GLP-1 Medications (Agonists)
These drugs mimic the natural hormone’s effects. Common examples include:
- Semaglutide (Ozempic®, Wegovy®, Rybelsus®)
- Liraglutide (Victoza®, Saxenda®)
- Dulaglutide (Trulicity®)
- Exenatide (Byetta®, Bydureon®)They are usually injectable (weekly or daily), though some oral forms exist.---### ⚕️ Why They’re Prescribed
- Type 2 Diabetes: Lower blood sugar and improve A1C levels.
- Obesity/Weight Management: Reduce appetite and promote weight loss.
- Additional Benefits: May lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol, and reduce risk of heart and kidney disease.---### ⚠️ Side Effects & Risks
- Common: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite.
- Rare but serious: Pancreatitis, thyroid cancer risk, kidney injury.
- Not approved for pregnancy.
- Can cause low blood sugar if combined with insulin or sulfonylureas.---### 🧩 Big Picture
GLP-1 is part of the incretin system, a set of hormones that fine-tune blood sugar after meals. Because natural GLP-1 breaks down quickly (half-life ~2 minutes), scientists developed GLP-1 receptor agonists to extend its effects. These medications are now considered game-changers in managing diabetes and obesity, but they work best alongside diet and lifestyle changes.
Meals on Wheels is not a single federal or state program—it’s a nationwide network of about 5,000 local, community-based programs. These programs receive a mix of funding: about 35–37% comes from the federal government through the Older Americans Act Nutrition Program, which is administered by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. States then distribute those funds to local agencies, but most Meals on Wheels programs also rely heavily on state and local support, charitable donations, corporate partnerships, and volunteers.---### 🥗 What Meals on Wheels Is
- Core mission: Provides nutritious meals to homebound seniors and people with disabilities who cannot easily shop or cook for themselves.
- Services offered:
- Home-delivered meals (the classic “meals on wheels”).
- Congregate meals served in senior centers or community spaces.
- Wellness checks: Volunteers often provide social interaction and safety checks during delivery.
- Scale: Serves over 2 million seniors annually across the U.S..---### 🏛️ How It’s Funded
- Federal funding (Older Americans Act): Covers about one-third of costs nationwide. Funds flow from the federal government → state agencies → local providers.
- State & local support: Each state has its own formula for distributing funds, so the mix varies widely.
- Private donations & partnerships: Community fundraising, foundations, and corporate sponsors fill the gap.
- Volunteers: Essential to keeping costs low and ensuring personal connection.---### 📊 Federal vs. State Role
- Federal role: Provides baseline funding through the Older Americans Act Nutrition Program.
- State role: Administers those funds, decides allocation formulas, and may add state-level support.
- Local role: Actually runs the programs—nonprofits, senior centers, or community organizations deliver the meals.---### ✅ Key Takeaway
Meals on Wheels is not a single government program but a hybrid public-private network. Federal dollars help, but the majority of its strength comes from local communities, volunteers, and donations. That’s why the program can look slightly different depending on where you live.
A geek is someone deeply passionate about a specific interest (like tech, gaming, or comics), a nerd is more academically focused and intellectual, and a dork is socially awkward without necessarily having the intellectual or hobby-driven focus. They overlap, but each carries a distinct flavor of personality.---### 🧑💻 Geek
- Definition: A geek is someone with intense enthusiasm for a niche subject, often technology, gaming, or pop culture.
- Traits: Passionate, knowledgeable, sometimes obsessive about their chosen interest.
- Modern Connotation: Being a geek is often seen positively today—think “geek chic.” Tech-savvy geeks are celebrated in industries like software, gaming, and entertainment.
- Example: Someone who can build a custom PC, quote every line from Star Wars, or knows the ins and outs of comic book lore.---### 📚 Nerd
- Definition: A nerd is highly intellectual, academically inclined, and deeply knowledgeable in subjects like math, science, or literature.
- Traits: Intelligent, detail-oriented, sometimes introverted or socially awkward.
- Modern Connotation: Nerds are respected for their brains, though the stereotype still includes glasses, books, and social shyness.
- Example: A math whiz who spends weekends solving equations or a literature lover who can analyze Shakespeare in depth.---### 🤪 Dork
- Definition: A dork is socially awkward or clumsy, often lacking the intellectual or hobby-driven focus of geeks and nerds.
- Traits: Goofy, awkward, sometimes endearing.
- Modern Connotation: “Adorkable” has become a playful way to describe someone whose awkwardness is charming rather than embarrassing.
- Example: Someone who tells bad jokes at the wrong time or trips over their own shoelaces but is lovable for it.---### ⚖️ Comparison Table| Term | Focus Area | Social Perception | Modern Spin |
|--------|------------|------------------|-------------|
| Geek | Passion for hobbies/tech | Enthusiastic, niche expert | “Geek chic” – cool to be one |
| Nerd | Academic/intellectual | Smart but socially awkward | Respected for intelligence |
| Dork | Social awkwardness | Clumsy, goofy | “Adorkable” – awkward but lovable |---### 🌟 Key Takeaway
- Geeks = passion-driven specialists.
- Nerds = brainy intellectuals.
- Dorks = socially awkward but often endearing.These labels used to be insults, but today many people proudly embrace them as badges of identity and community.
Let’s break this down with some math and context:---### 💰 The Math
- Spending $1,000,000 per day:
- In one year: (1,000,000 \times 365 = 365,000,000) (≈ $365 million).
- To reach $1 trillion:
[
\frac{1,000,000,000,000}{365,000,000} \approx 2,740 \text{ years}
]
- So yes — it would take about 2,740 years, which is close to the “almost 3,000 years” claim. ✅---### 🏦 The Point About “Earning” $1 Trillion
- No individual has ever “earned” $1 trillion in wages or salary.
- The richest people in the world (Elon Musk, Jeff Bezos, etc.) have net worths in the hundreds of billions, not trillions. Their wealth comes from ownership of assets (stocks, companies, investments), not from “working” in the traditional sense.
- Wealth at that scale is structural: it’s tied to capital appreciation, monopolistic control, and financial systems — not labor hours.---### ⚖️ The Nuance
- The math is correct: $1 trillion is so vast that even absurd daily spending barely dents it.
- The statement “No one earns or works for that” is more of a political/economic critique than a literal fact. It’s pointing out that trillion-level wealth is systemic and financial, not the result of personal effort.---📌 Bottom Line:
Yes, the math checks out — spending $1M/day would take nearly 3,000 years to exhaust $1 trillion. And it’s true that no one “works” their way to that kind of wealth; it’s accumulated through ownership, investments, and systems of capital, not wages or labor.
The statement is partly true but oversimplified. Private insurance in the U.S. can and does deny claims, sometimes leading to financial hardship or bankruptcy. Single-payer universal healthcare systems generally reduce or eliminate this risk, but they are not entirely free of limitations or challenges.---### 🏥 Private Insurance Realities
- Claim Denials: In the U.S., insurance companies frequently deny claims. A 2023 analysis found that millions of Americans had claims denied, often through automated systems or arbitrary reviews.
- Financial Risk: Medical debt is a leading cause of bankruptcy in the U.S. Even insured patients can face high deductibles, copays, and uncovered services.
- Complexity: Patients often must navigate appeals processes, surprise bills, and coverage loopholes. This creates uncertainty and financial vulnerability.### 🌍 Single-Payer Universal Healthcare
- Coverage Guarantee: In single-payer systems (like Canada’s Medicare or the UK’s NHS), the government is the primary payer. This means essential care is covered for all citizens, and patients don’t face claim denials in the same way.
- Reduced Bankruptcy Risk: Because care is funded publicly, individuals are shielded from catastrophic medical bills. Bankruptcy due to medical expenses is rare in countries with single-payer systems.
- Limitations: However, single-payer systems may face wait times, rationing of certain elective procedures, or limited coverage for non-essential services. So while they prevent financial ruin, they are not “perfect” or without trade-offs.### ⚖️ The Nuance
- Saying “insurance can deny claims and bankrupt you” is accurate in the U.S. context.
- Saying “single-payer won’t, period” is too absolute. Single-payer systems do protect against medical bankruptcy, but they may still limit access to certain treatments or require waiting periods.---### 📌 Bottom Line
- True: U.S. private insurance can deny claims, leaving patients financially vulnerable.
- Mostly True: Single-payer universal healthcare prevents medical bankruptcy and claim denials for essential care.
- Not Entirely True: Single-payer systems still have constraints (wait times, coverage limits), so “won’t, period” oversimplifies the reality.
---### 🏥 Private Insurance Realities
- Claim Denials: In the U.S., insurance companies frequently deny claims. A 2023 analysis found that millions of Americans had claims denied, often through automated systems or arbitrary reviews.
- Financial Risk: Medical debt is a leading cause of bankruptcy in the U.S. Even insured patients can face high deductibles, copays, and uncovered services.
- Complexity: Patients often must navigate appeals processes, surprise bills, and coverage loopholes. This creates uncertainty and financial vulnerability.### 🌍 Single-Payer Universal Healthcare
- Coverage Guarantee: In single-payer systems (like Canada’s Medicare or the UK’s NHS), the government is the primary payer. This means essential care is covered for all citizens, and patients don’t face claim denials in the same way.
- Reduced Bankruptcy Risk: Because care is funded publicly, individuals are shielded from catastrophic medical bills. Bankruptcy due to medical expenses is rare in countries with single-payer systems.
- Limitations: However, single-payer systems may face wait times, rationing of certain elective procedures, or limited coverage for non-essential services. So while they prevent financial ruin, they are not “perfect” or without trade-offs.### ⚖️ The Nuance
- Saying “insurance can deny claims and bankrupt you” is accurate in the U.S. context.
- Saying “single-payer won’t, period” is too absolute. Single-payer systems do protect against medical bankruptcy, but they may still limit access to certain treatments or require waiting periods.---### 📌 Bottom Line
- True: U.S. private insurance can deny claims, leaving patients financially vulnerable.
- Mostly True: Single-payer universal healthcare prevents medical bankruptcy and claim denials for essential care.
- Not Entirely True: Single-payer systems still have constraints (wait times, coverage limits), so “won’t, period” oversimplifies the reality.
Short answer:* Yes — 70% isopropyl alcohol is effective for disinfecting toilet surfaces, but it’s best used for quick sanitizing rather than heavy-duty cleaning.---### 🧴 Why 70% Isopropyl Alcohol Works
- Optimal concentration: 70% alcohol is considered the gold standard for disinfection because the water content slows evaporation, allowing more contact time to penetrate microbial cell walls and kill bacteria, fungi, and many viruses.
- Broad-spectrum action: It is rapidly bactericidal, fungicidal, and virucidal, making it suitable for everyday sanitization.
- Surface suitability: Alcohol is safe for most hard, non-porous bathroom surfaces like toilet seats, handles, and flush buttons.---### 🚫 Limitations You Should Know
- Not effective against spores: Alcohol does not kill bacterial spores (e.g., Clostridium difficile), which can sometimes be present in bathrooms.
- No cleaning power: Alcohol disinfects but doesn’t remove dirt, stains, or mineral deposits. Toilets often need a cleaner + disinfectant combo.
- Flammability: Isopropyl alcohol is highly flammable — avoid spraying near open flames or hot surfaces.
- Strong odor: Ventilate the bathroom when using it to avoid inhaling fumes.---### ✅ Best Practices for Toilet Disinfection
- Step 1: Clean first. Use a toilet cleaner or soap solution to remove visible soil and organic matter.
- Step 2: Disinfect. Spray 70% isopropyl alcohol on the seat, handle, and exterior surfaces. Let it sit for at least 30 seconds to 1 minute before wiping.
- Step 3: Repeat regularly. Alcohol is great for daily or quick sanitizing, but for deeper disinfection (especially inside the bowl), use bleach-based or EPA-registered bathroom disinfectants.---### 🐾 Bottom Line
70% isopropyl alcohol in a spray bottle is excellent for quick toilet surface disinfection — especially for handles, seats, and lids. However, it should be paired with a proper toilet cleaner for thorough hygiene, since alcohol alone doesn’t tackle spores or heavy grime.
McDonald’s wasn’t originally designed as a “starter job,” but over time it became widely seen that way because of its accessibility, flexible scheduling, and the transferable skills it teaches. The company itself now embraces the idea, branding itself as “America’s Best First Job.”---### 🏗️ Origins of McDonald’s Jobs
- When McDonald’s expanded in the 1950s–60s, the jobs were simply restaurant crew positions needed to run a fast-growing fast-food chain.
- The intent wasn’t specifically to create “starter jobs” for teens; it was about staffing restaurants efficiently.
- Early on, many employees were adults, including women entering the workforce in part-time roles, not just teenagers.### 📌 Why It Became Seen as a Starter Job
- Accessibility: No advanced education or prior experience is required, making it a natural entry point for young workers.
- Flexible scheduling: Fits around school hours, which appeals to high school and college students.
- Skill development: Employees learn teamwork, customer service, problem-solving, and time management — all transferable to other careers.
- Scale: With thousands of locations, McDonald’s became one of the most common first employers. In fact, 1 in 8 Americans have worked at McDonald’s at some point.### 🏅 McDonald’s Own Branding
- McDonald’s now actively markets itself as “America’s Best First Job”, highlighting the soft skills and career pathways it offers.
- Programs like Archways to Opportunity provide education benefits, including high school diplomas, college tuition assistance, and English-language learning.
- This reinforces the perception that McDonald’s is not just a job, but a stepping stone toward future opportunities.### ⚖️ The Cultural Perception
- Society often labels fast-food work as “low skill” or temporary, which contributes to the “starter job” stereotype.
- Yet many employees stay long-term, moving into management or franchise ownership. McDonald’s emphasizes that it can be both a first job and a career path.
- Reviews from workers often describe it as a great starter job or stepping stone, but also note challenges like stress during busy hours.---✅ In summary: McDonald’s jobs weren’t meant to be starter jobs, but the combination of accessibility, flexibility, and skill-building made them the quintessential first job for millions. The company now embraces that identity while also promoting long-term career growth.
A dork is usually someone who’s socially awkward, clumsy, or goofy, while a nerd is someone who’s highly intellectual, academically inclined, and deeply passionate about specific subjects. Both can overlap, but the emphasis is different: dorks are defined more by social quirks, nerds by intellectual focus.🧩 Breaking It Down
1. Definition
Dork:
Informal term for someone socially inept, awkward, or unfashionable.
Often associated with clumsiness or eccentric behavior.
Interests may be quirky, niche, or fandom-related.
Nerd:
Someone intelligent and academically focused.
Deeply passionate about subjects like science, math, literature, or technology.
May be socially awkward, but the defining trait is intellectual enthusiasm.
2. Social Perception
Dorks are often seen as goofy or “adorkable,” sometimes endearing but not necessarily respected for knowledge.
Nerds may be admired for expertise, especially in academic or technical circles, though historically stereotyped as introverted or uncool.
3. Interests & Passions
Dorks: More about personality quirks—liking odd hobbies, being clumsy, or socially offbeat.
Nerds: More about intellectual pursuits—coding, physics, chess, or any subject requiring deep study.
4. Modern Reclamation
Both terms were once insults, but today they’re often worn proudly.
“Nerd culture” is mainstream (think Marvel, gaming, coding).
“Dork” has been softened into a playful, affectionate label (“you’re such a dork!”).⚖️ Side-by-Side Comparison
Trait
Dork 🕺
Nerd 📚
Core Identity
Socially awkward, goofy
Academically/intellectually focused
Interests
Niche hobbies, fandoms
Science, math, literature, tech
Social Perception
Clumsy, eccentric, sometimes endearing
Smart, knowledgeable, sometimes introverted
Modern Use
Playful, affectionate insult
Badge of honor in tech/academic circlesSo, if someone trips over their shoelaces while excitedly talking about their favorite cartoon, they’re acting like a dork. If someone spends hours happily solving equations or coding a game, they’re being a nerd. Of course, plenty of people are both—and that overlap is where the fun begins.
Yes, that’s true. Most of the oxygen we breathe actually comes from the ocean, not forests. Tiny marine organisms called phytoplankton are responsible for producing 50–80% of Earth’s oxygen, and NASA actively tracks them from space because of their enormous role in sustaining life and regulating climate.---### 🌊 Ocean vs. Forest Oxygen Production
- Forests (like the Amazon): Often called the “lungs of the Earth,” but they contribute a smaller share of global oxygen compared to oceans. Forests are vital for biodiversity and carbon storage, but their net oxygen contribution is less than commonly assumed because respiration and decomposition consume much of what they produce.
- Phytoplankton: Microscopic algae and cyanobacteria floating in the ocean. Through photosynthesis, they release oxygen into the atmosphere.
- Estimates suggest they generate over half of Earth’s oxygen supply.
- They also absorb massive amounts of carbon dioxide, helping regulate climate.### 🌱 Prochlorococcus: The Tiny Powerhouse
- Prochlorococcus is a single-celled cyanobacterium found in oceans worldwide.
- Despite its microscopic size, it’s the most abundant photosynthetic organism on Earth.
- Scientists estimate it alone contributes about 20% of the oxygen in our atmosphere—meaning one in five breaths you take could be thanks to this species.### 🛰️ NASA’s Role
- NASA monitors phytoplankton using satellites like PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem).
- These satellites measure ocean color and light reflection to identify where phytoplankton are thriving.
- Tracking them is crucial because phytoplankton populations shift with climate change, ocean temperature, and nutrient availability.
- Without them, Earth’s oxygen balance and food chains would collapse.### 🌍 Why This Matters
- Climate regulation: Phytoplankton absorb carbon dioxide, slowing global warming.
- Food webs: They are the base of the marine food chain, feeding everything from tiny zooplankton to whales.
- Human survival: The oxygen they produce is essential for life on land.---✅ In summary: The claim is correct—oceans, via phytoplankton, are the dominant source of Earth’s oxygen, with Prochlorococcus alone making a staggering contribution. Forests are still vital for ecosystems and carbon storage, but when it comes to oxygen, the ocean is the real “lung of the planet.”
Yes — Gmail just tightened its rules for bulk email senders in November 2025. This change is causing ripple effects across the email ecosystem, and you may be seeing more marketing emails slip through because companies are scrambling to comply with Google’s new enforcement policies.---### 📩 What Changed in Gmail Recently
- New Enforcement Phase (Nov 2025)
Gmail moved from a “soft enforcement” mode to strict rejection and bounce handling for emails that don’t meet authentication standards like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC.
- Impact on Bulk Senders
Until now, non-compliant marketing emails often went straight to spam. Now, Gmail is actively rejecting them at the protocol level. Some senders are overcorrecting or changing their systems, which can result in legitimate-looking but unsolicited emails landing in inboxes.
- Unsubscribe & Transparency Requirements
Gmail is also requiring clearer unsubscribe links and sender identification. Companies rushing to comply may be sending out more “confirmation” or “welcome” style emails, even if you never signed up.---### 🔎 Why You’re Seeing More Emails
- Misconfigured Senders: Some companies may have updated their systems incorrectly, causing emails to bypass spam filters.
- List Pollution: Your address may have been added to marketing lists without consent (a common issue when enforcement rules change).
- Authentication Shifts: As Gmail enforces stricter standards, some senders who previously landed in spam are now slipping into the inbox until they’re fully blocked.---### ✅ What You Can Do
- Mark as Spam: Each time you mark one of these emails as spam, Gmail’s filters learn and adjust.
- Check Filters: In Gmail settings, you can create filters to automatically delete or archive emails with certain keywords (like “newsletter” or “welcome”).
- Unsubscribe Carefully: If the sender looks legitimate, use the unsubscribe link. If it looks suspicious, avoid clicking links and just mark as spam.
- Monitor Account Security: While this influx is likely due to Gmail’s policy changes, it’s always wise to check your Google Account’s recent activity to ensure your email hasn’t been compromised.---### 📌 Bottom Line
You didn’t suddenly sign up for dozens of mailing lists — this is fallout from Gmail’s November 2025 bulk sender compliance enforcement. Companies are adjusting, and some unwanted emails are slipping through. The situation should stabilize as Gmail continues rejecting non-compliant senders and marketers clean up their practices.
Short answer: No—most of the people who benefited from the COVID-era ACA expansion will not automatically “make enough money” or have other healthcare once it expires. The enhanced subsidies were designed to help middle-income households who still struggled with premiums, and without them, millions will face sharply higher costs or lose coverage altogether.---### 🩺 What the COVID-era ACA expansion did
- In 2021, Congress passed the American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA), which temporarily expanded ACA subsidies.
- It capped premiums at 8.5% of household income for marketplace plans, regardless of income level.
- This meant even middle-income families (earning above 400% of the federal poverty level) could qualify for help if premiums were high in their area.
- The expansion was later extended through 2025 by the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA).### 📉 What happens if it expires after 2025
- Premiums will spike: On average, ACA enrollees could see premiums rise by over 100% in 2026.
- Coverage loss: Millions who enrolled during the pandemic thanks to lower costs may drop coverage entirely.
- Middle-class impact: Many of those who qualified under the expansion are not “poor” but still don’t have employer coverage. They’ll be squeezed hardest because they’ll lose subsidies but still face high premiums.
- Insurers & markets: The expiration could destabilize ACA marketplaces, with fewer healthy enrollees and higher costs overall.### 💡 Why “COVID is over” doesn’t mean people no longer need help
- The subsidies weren’t tied to COVID infection rates—they were tied to economic affordability.
- Even post-pandemic, healthcare costs keep rising faster than wages.
- Many workers in gig jobs, small businesses, or part-time roles still lack employer-sponsored insurance.
- Without subsidies, a family making $60,000–$80,000 could face premiums of $800–$1,200 per month—unrealistic for many budgets.### 🔑 Key takeaway
The COVID-era ACA expansion wasn’t just a temporary “pandemic fix.” It addressed a long-standing affordability gap for middle-income Americans. If it expires, millions will be priced out of coverage, not because they suddenly earn more, but because premiums remain high while subsidies vanish.---
Yes, plums are considered a low-glycemic fruit. Their glycemic index (GI) is typically around 24–35, which falls well below the threshold for low GI foods (55 or less). This means they cause only a slow, gradual rise in blood sugar levels. Plums also have a low glycemic load (about 3.9 per 100g), making them a good choice for people managing blood sugar or following a low-GI diet.12Fresh plums are best because they contain fiber, vitamins (A, C, K), potassium, and antioxidants that help slow sugar absorption and support overall health. Dried plums (prunes), however, are more calorie-dense and have a higher glycemic impact, so they should be eaten in moderation.
Forest Whitaker’s distinctive eye appearance is caused by a condition called ptosis, a congenital drooping of the upper eyelid that affects his left eye. It’s not the result of an accident or illness later in life—he was born with it and has chosen not to undergo corrective surgery.---### 🌟 Breaking It Down
- Medical term: Ptosis (also known as blepharoptosis)
- What it is: A condition where the upper eyelid droops lower than normal, sometimes partially covering the eye.
- Whitaker’s case: His left eyelid has ptosis from birth, which has mildly impaired his vision but never stopped him from thriving in his career.
- Surgery option: Ptosis can be corrected surgically, but Whitaker has decided against it, embracing his natural look.---### 👁️ Why It Stands Out
- Unique appearance: His eye has become part of his recognizable screen presence, adding depth and intensity to his characters.
- Career impact: Far from holding him back, Whitaker has won an Academy Award, BAFTA, and Golden Globe, proving that his talent overshadows any physical difference.
- Public perception: While some fans speculate about his eye, Whitaker himself has treated it as a non-issue, focusing on his craft and humanitarian work.---### 🧬 Causes of Ptosis
- Congenital (from birth): As in Whitaker’s case, often due to underdeveloped muscles that lift the eyelid.
- Acquired: Can also occur later in life from trauma, nerve damage, cataract surgery, or long-term contact lens use.
- Severity: Ranges from mild cosmetic drooping to significant vision impairment, depending on how much the eyelid covers the pupil.---### 🌍 Bigger Picture
Whitaker’s story is a reminder that visible differences don’t define ability or success. Many other public figures also have ptosis—such as Thom Yorke (Radiohead) and Paris Hilton—and have turned it into part of their unique identity.---✅ In short: Forest Whitaker’s eye condition is congenital ptosis, a drooping eyelid he’s had since birth. It hasn’t limited his career or life, and he’s chosen to embrace it rather than change it.
Diamonds are not especially rare compared to other gemstones. They are actually one of the most common precious stones found in nature, but their perceived rarity has been shaped largely by marketing and controlled supply.---### 💎 How Common Are Diamonds?
- Geological abundance: Diamonds are made of carbon, one of the most common elements on Earth. While gem-quality diamonds require specific conditions to form, industrial-quality diamonds are relatively abundant.
- Compared to other gems: Diamonds are far more common than rubies, emeralds, or sapphires. Those colored gemstones are genuinely rarer in nature.
- Annual production: Each year, over 100 million carats of natural diamonds are mined worldwide. On top of that, lab-grown diamonds are increasingly common, further boosting availability.---### 📈 Why Do People Think Diamonds Are Rare?
- De Beers marketing: In the early 20th century, the De Beers company tightly controlled diamond supply and launched the famous “A diamond is forever” campaign. This created the cultural association of diamonds with love, rarity, and value.
- Controlled supply: By limiting how many diamonds entered the market, companies maintained high prices despite the relative abundance of stones.
- Psychological value: Diamonds became the default engagement stone, which reinforced the idea that they were unique and precious.---### 🌈 What Is Rare in Diamonds?
- Fancy colors: While clear diamonds are common, natural fancy-colored diamonds (blue, pink, red, green) are extremely rare and command very high prices.
- Large flawless stones: Big diamonds with perfect clarity and cut are much less common than smaller, slightly flawed ones.---### ✅ Key Takeaways
- Ordinary diamonds are not rare — they are one of the most common gemstones.
- Their high value is cultural and economic, not geological.
- Truly rare diamonds are those with unusual colors or exceptional size/quality.---
The claim that Michelle Obama is male is a baseless conspiracy theory that has circulated in some conservative circles since at least 2008. It is not supported by any evidence and has been repeatedly debunked by fact-checkers.---### 📌 Why This Conspiracy Exists
- Political Smear Tactic: Conspiracy theories about Michelle Obama’s gender identity are primarily used as a way to demean or delegitimize her and, by extension, Barack Obama. They rely on mockery and innuendo rather than facts.
- Racist & Sexist Undertones: Many analysts point out that these claims are rooted in racist and sexist stereotypes—portraying a tall, athletic Black woman as “too masculine” to be female.
- Viral Disinformation: False claims have spread through doctored photos, edited videos, and fake documents. For example:
- A doctored voter registration record supposedly showing Michelle Obama as male was proven fake by the Illinois State Board of Elections.
- A manipulated photo circulated online to make her appear more masculine.
- A clipped podcast video was taken out of context to suggest she called herself a man, which she did not.---### 🧩 Why Some Republicans Amplify It
- Culture War Politics: For certain far-right commentators, pushing this conspiracy fits into broader attacks on LGBTQ+ issues, gender identity, and progressive politics.
- Echo Chamber Effect: Once a false claim gains traction in partisan media or online communities, it gets repeated until it feels “true” to those inside the bubble.
- Delegitimizing Opponents: By questioning Michelle Obama’s identity, conspiracy theorists attempt to undermine her credibility, her husband’s presidency, and the Democratic Party more broadly.---### ✅ The Reality
- Michelle Obama was born Michelle LaVaughn Robinson on January 17, 1964, in Chicago, Illinois.
- She has lived her entire public and private life as a woman, including her education at Princeton and Harvard, her legal career, her role as First Lady, and her family life raising two daughters.
- Multiple independent fact-checking organizations (AFP, Snopes, Factually, Yahoo News) have debunked these claims repeatedly.---### 🔎 Why It Persists
Conspiracy theories often survive because they are emotionally charged, easy to spread, and hard to disprove to those who want to believe them. In this case, the theory combines elements of misogyny, racism, and political polarization, which makes it a convenient tool for some partisan actors.---👉 In short: Republicans who push this claim aren’t relying on facts—they’re using a conspiracy theory as a political weapon.
Quick Answer: The human body naturally produces several “dangerous” chemicals as part of normal metabolism. These include free radicals (reactive oxygen species), ammonia, carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and even formaldehyde in trace amounts. While toxic in high concentrations, they play essential roles in signaling, energy production, and defense when tightly regulated.---### ⚗️ Key “Dangerous” Chemicals Made by the Body
Here are some of the most notable ones:- Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
- Examples: superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radicals
- Danger: Highly reactive, can damage DNA, proteins, and cell membranes.
- Role: Used by immune cells to kill pathogens; also act as signaling molecules.- Ammonia (NH₃)
- Danger: Neurotoxic at high levels; buildup can cause confusion, coma, or death.
- Role: Produced during protein metabolism; normally converted to urea in the liver and excreted in urine.- Carbon Monoxide (CO)
- Danger: Binds hemoglobin more strongly than oxygen, leading to hypoxia.
- Role: Surprisingly, the body makes small amounts during breakdown of hemoglobin; acts as a signaling molecule in blood vessel regulation.- Hydrogen Sulfide (H₂S)
- Danger: Known as “rotten egg gas,” toxic at high concentrations.
- Role: At low levels, functions as a neuromodulator and helps regulate blood pressure.- Formaldehyde
- Danger: Carcinogenic in high exposure.
- Role: Produced in tiny amounts during amino acid metabolism; detoxified quickly by enzymes.- Bilirubin & Biliverdin
- Danger: Excess bilirubin causes jaundice and can damage the brain in infants.
- Role: Normal breakdown products of hemoglobin; also act as antioxidants.- Histamine
- Danger: Excess release can cause allergic reactions, anaphylaxis.
- Role: Essential for immune response, stomach acid regulation, and neurotransmission.---### 🧩 Why the Body Makes Them
- Defense: Free radicals and nitric oxide help immune cells kill bacteria.
- Signaling: CO, H₂S, and nitric oxide act as “gasotransmitters,” regulating blood vessels and nerves.
- Metabolism: Ammonia and formaldehyde are unavoidable byproducts of breaking down proteins and amino acids.---### ⚠️ The Balance Factor
The key is dose and regulation.
- At low, controlled levels, these chemicals are vital for survival.
- At high, uncontrolled levels, they become toxic and contribute to diseases like cancer, neurodegeneration, or organ failure.---In short: The body is a paradoxical chemist—it constantly produces substances that could kill us if they weren’t tightly managed, yet those same substances are indispensable for keeping us alive.
Yes, some vaccines contain trace amounts of formaldehyde. It’s used to inactivate viruses and detoxify bacterial toxins, but the residual levels are tiny compared to what your body naturally produces and safely clears. The body metabolizes and eliminates it quickly, so the amounts in vaccines are not considered dangerous.---### 🧪 Why Formaldehyde Is Used
- Purpose: Formaldehyde is used during vaccine manufacturing to inactivate viruses (so they can’t cause disease) and to neutralize bacterial toxins (like diphtheria toxin).
- Residuals: After purification, only trace amounts remain in the final vaccine dose.---### 📊 How Much Is in Vaccines
- Typical vaccines contain less than 0.005–0.1 mg per dose.
- For comparison:
- A 2-month-old infant naturally has about 1.1 mg of formaldehyde circulating in their blood—that’s 10–220 times more than what’s in a single vaccine dose.
- Everyday foods and environmental exposure add far more formaldehyde than vaccines do.---### ⚠️ At What Level Is It Dangerous
- High concentrations of formaldehyde (like in industrial exposure or inhalation at workplaces) can damage DNA and increase cancer risk.
- Vaccine levels are far below danger thresholds:
- Animal studies show doses 600 times greater than vaccine amounts are still safe.
- Regulatory agencies (FDA, CDC, WHO) confirm that vaccine formaldehyde levels are not harmful.---### 🩺 Does the Body Get Rid of It?
- Yes. Formaldehyde is a natural byproduct of metabolism. Your body continuously produces and breaks it down as part of normal processes (like making amino acids and DNA).
- After vaccination, studies show formaldehyde at the injection site is cleared within 30 minutes, and blood levels remain less than 1% of natural background levels.
- The body doesn’t distinguish between “vaccine formaldehyde” and “natural formaldehyde”—it processes both the same way.---### ✅ Key Takeaways
- Formaldehyde is present in some vaccines, but only in trace amounts.
- It’s essential for safe vaccine production (inactivating viruses/toxins).
- Levels are far below harmful thresholds and much less than what your body naturally carries.
- Your body quickly eliminates it, so it doesn’t accumulate or pose a risk.
Quick Answer: The most accessible fruit with one of the best all-around nutritional packages is the banana—widely available year-round, inexpensive, and packed with potassium, fiber, vitamin B6, and quick energy. Close contenders are apples and oranges, which are equally easy to find and provide excellent vitamin C, fiber, and antioxidants.---### 🍌 Why Bananas Stand Out
- Availability: Found in nearly every grocery store worldwide, affordable, and available year-round.
- Nutrients:
- High in potassium (supports heart health and blood pressure).
- Good source of vitamin B6 (important for metabolism and brain health).
- Provides dietary fiber (aids digestion).
- Natural sugars + carbs = quick, sustained energy.
- Convenience: Comes in its own “packaging,” no prep required.---### 🍎 Apples – The Everyday Powerhouse
- Nutrients:
- Rich in fiber (especially pectin, which supports gut health).
- Contains vitamin C and antioxidants that reduce inflammation.
- Benefits: Linked to lower risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
- Practicality: Stores well, portable, and available in many varieties.---### 🍊 Oranges – The Immune Booster
- Nutrients:
- Excellent source of vitamin C (supports immunity and skin health).
- Provides folate and potassium.
- Benefits: Antioxidants in oranges help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation.
- Practicality: Widely available, especially in winter months, and can be eaten fresh or juiced.---### 🫐 Honorable Mention: Blueberries
- Nutrients: Extremely high in antioxidants (anthocyanins), vitamin C, and fiber.
- Benefits: Strong evidence for brain health, heart health, and reducing oxidative stress.
- Limitation: More expensive and seasonal compared to bananas, apples, and oranges.---### ✅ Bottom Line
If you want the easiest-to-obtain fruit with the best nutritional balance, bananas are the clear winner. For a well-rounded daily mix, pairing bananas with apples or oranges covers potassium, fiber, vitamin C, and antioxidants—an affordable, powerhouse trio for everyday health.
No—unborn children are not considered parasites in the biological or medical sense. While some people use the term metaphorically in debates about pregnancy, the scientific definition of a parasite does not apply to a human fetus.---### 🔬 Why the Term “Parasite” Doesn’t Fit
- Definition of parasite: A parasite is an organism that lives in or on a host of a different species and typically harms the host while benefiting itself. Examples include tapeworms, lice, or malaria-causing protozoa.
- Fetuses are the same species: An unborn child is genetically human, sharing the same species as the mother. This alone disqualifies it from being a parasite under the biological definition.
- Mutual biological relationship: Research shows that fetal cells can actually benefit the mother. For example, fetal stem cells sometimes migrate into the mother’s body and help repair tissues, including the heart and liver.---### ⚖️ Why the Term Is Sometimes Used
- Metaphorical use in debates: Some pro-choice advocates use the word “parasite” rhetorically to emphasize the fetus’s dependence on the mother’s body and the fact that pregnancy is not voluntary for all women.
- Philosophical framing: Abortion provider Warren Hern once described the mother–fetus relationship as “host and parasite” to highlight bodily autonomy issues. This is not a scientific claim but a philosophical or political framing.
- Cultural pushback: Many ethicists, religious groups, and medical professionals reject the term as dehumanizing, arguing that it ignores the unique biological and social relationship between mother and child.---### 🌱 A More Accurate Framing
- Dependent, not parasitic: A fetus is better described as dependent on the mother rather than parasitic. Dependence is a normal part of human development, just as infants and children remain dependent after birth.
- Unique biological bond: Unlike parasites, which exploit hosts, pregnancy is a natural reproductive process that has evolved to sustain both mother and child.---✅ In summary: Scientifically, unborn children are not parasites because they are the same species as their mother and the relationship is not inherently harmful. The term is sometimes used metaphorically in ethical or political debates, but it is not accurate in a biological sense.
Yes—ignorance often fuels hatred. A lack of knowledge or understanding about others can breed fear, stereotypes, and intolerance, which in turn can harden into hatred. But ignorance alone isn’t always the cause; it usually works together with fear, insecurity, or lack of empathy.---### 🔍 How Ignorance Connects to Hatred
- Psychological roots: Research shows that hate can come from ignorance and lack of exposure to different cultures, beliefs, and ways of life. When people don’t understand others, they may fill the gap with assumptions, often negative ones.
- Fear of the unknown: Ignorance creates uncertainty, and uncertainty often triggers fear. Fear, when left unchecked, can morph into hostility or hatred.
- Dehumanization: Without knowledge or empathy, it’s easier to see others as “different” or “less than,” which makes hateful attitudes more likely.
- Reinforcement loops: Ignorance can lead to prejudice, which then justifies avoiding contact with others—keeping ignorance alive and deepening hatred.---### 🧘 Spiritual and Philosophical Views
- Buddhism’s “Three Poisons”: In Buddhist thought, ignorance, greed, and hatred are seen as the root causes of suffering. Ignorance clouds perception, which allows hatred to arise.
- Moral philosophy: Many traditions argue that hatred is not innate but learned, often through misinformation, lack of education, or willful blindness.---### 📚 Breaking the Cycle
- Education & exposure: Learning about different cultures, histories, and perspectives reduces ignorance and weakens the soil where hatred grows.
- Empathy-building: Direct contact with people from different backgrounds often dissolves stereotypes.
- Critical thinking: Recognizing that opinions aren’t facts helps prevent ignorance from hardening into dogma.---### ⚖️ The Nuance
It’s important to note that ignorance doesn’t always lead to hatred. Sometimes it leads to indifference, curiosity, or even humility. Hatred usually requires an added spark—fear, resentment, or manipulation by others. But ignorance makes people more vulnerable to those sparks.---So, in short: ignorance is not the sole cause of hatred, but it’s a powerful enabler. Hatred thrives where understanding is absent, and it weakens when knowledge, empathy, and dialogue take root.
Short answer: Raising wages can lead to higher prices, but the effect is usually modest and depends on the industry, timing, and broader economic conditions. In many cases, businesses absorb some of the costs through productivity gains or reduced turnover, so the price impact is smaller than people often assume.---### 🔑 Key Points to Understand- Cost-Push Effect:
When wages rise, especially through minimum wage laws, businesses face higher labor costs. Some of these costs may be passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices. This is most visible in labor-intensive industries like restaurants, retail, and hospitality.- Magnitude of Price Increases:
Research shows the price pass-through effect is relatively small and often temporary. For example, studies by the Upjohn Institute found that while prices may rise slightly after a wage hike, the effect tends to fade as businesses adjust through efficiency improvements, automation, or reduced turnover.- Offsetting Factors:
- Lower turnover and training costs: Higher wages reduce employee churn, saving businesses money.
- Productivity gains: Better-paid workers are often more motivated and productive.
- Consumer demand boost: Workers with higher wages spend more, which can increase sales and offset higher costs.- Inflation vs. Wages:
Over the past few years, wages in many sectors have risen faster than prices, especially for lower-income workers. This means that while some prices did increase, workers’ purchasing power often improved overall.- Industry Differences:
- Restaurants & fast food: Prices tend to rise more noticeably here, since wages are a large share of costs.
- Manufacturing & tech: Less impact, because labor is a smaller portion of total costs.- Policy Design Matters:
Gradual, predictable wage increases give businesses time to adapt, leading to smaller price effects. Sudden, large hikes can create sharper short-term price adjustments.---### 📊 Bottom Line
Raising wages does not automatically cause runaway inflation. Yes, some prices may rise, but usually by a small margin—and the benefits of higher wages (reduced turnover, stronger consumer demand, improved worker well-being) often outweigh the modest price increases. The real-world impact depends heavily on the sector and how businesses adapt.---
Yes. European diseases—brought by early explorers and later the Pilgrims—devastated the Wampanoag and other Native peoples, killing the majority of their population before and after the Mayflower’s arrival.---### 🦠 The Epidemics Before the Pilgrims
- Between 1616 and 1619, just before the Pilgrims landed, a mysterious epidemic swept through coastal New England. Historians call this the “Great Dying.”
- It killed an estimated two-thirds to 90% of the Native population in the region, including many Wampanoag communities.
- The exact disease is debated. Some scholars suggest smallpox, others propose leptospirosis (a bacterial infection spread by rat urine), or other European-borne illnesses.### 🚢 When the Pilgrims Arrived
- By the time the Mayflower landed in 1620, the Pilgrims found abandoned villages and cleared fields where thriving Wampanoag communities had once lived.
- This depopulation was not caused by warfare but by disease introduced through earlier European contact—fishermen, traders, and explorers who had been visiting New England’s coast for decades before the Pilgrims.### 📉 Impact on the Wampanoag
- The Wampanoag Confederacy, once numbering in the tens of thousands, was reduced to only a few thousand survivors.
- This catastrophic loss weakened them militarily and socially, forcing Chief Massasoit to ally with the Pilgrims in 1621 for survival against stronger rivals like the Narragansett.
- Even after the Pilgrims’ arrival, new waves of disease continued to strike Native communities throughout the 17th century, further eroding their population and autonomy.### ⚖️ The Larger Context
- Across the Americas, disease was the single greatest factor in the collapse of Indigenous populations after European contact.
- Unlike Europeans, Native peoples had no prior exposure to Old World pathogens like smallpox, measles, influenza, and plague, so they had no immunity.
- Historians estimate that up to 90% of Indigenous people in North America died from disease between the 1500s and 1700s.---✅ In short: The Pilgrims themselves did not deliberately unleash disease, but their arrival was part of a broader wave of European contact that introduced deadly pathogens. For the Wampanoag, these epidemics were catastrophic—killing most of their people and reshaping the balance of power in New England.
Short answer: The perception that SNAP users “only buy junk food” is a stereotype, not reality. While some SNAP dollars do go toward soda, snacks, and convenience foods, research shows that SNAP households buy food in patterns very similar to non-SNAP households. The stigma comes from a mix of politics, media framing, and cultural biases about poverty, not from the actual shopping carts of most recipients.🔎 Why the Stereotype Exists
Media Narratives: News stories often highlight extreme or sensational examples—like someone using benefits to buy soda in bulk—rather than the everyday reality of families buying bread, milk, eggs, and produce.
Political Debates: SNAP has long been a lightning rod in U.S. politics. Proposals to restrict “junk food” purchases reinforce the idea that recipients are irresponsible, even though data shows otherwise.
Class & Poverty Bias: There’s a cultural tendency to scrutinize the spending of low-income people more harshly than middle- or upper-income shoppers. When wealthier households buy chips or soda, it’s seen as a personal choice; when SNAP users do, it’s framed as wasteful.
Visibility of Purchases: SNAP purchases are made with EBT cards, which can make them more noticeable at checkout. That visibility feeds into judgment and stigma.📊 What the Data Actually Shows
Top SNAP Purchases: According to USDA data, the most common items include milk, bread, chicken, cheese, and fresh produce—the same staples bought by non-SNAP households.
Soda & Snacks: Yes, soft drinks and snack foods appear in the top categories, but they do for everyone. In fact, non-SNAP households spend nearly the same share of their grocery budget on these items.
Overall Diet Quality: Studies find that SNAP participants’ diets are only slightly less healthy than the national average, largely due to broader issues of food access and affordability, not misuse of benefits.⚖️ Why the Perception Persists
Policy Pushes: Campaigns like “Make America Healthy Again” have pushed to ban soda and candy from SNAP, which reinforces the idea that SNAP users are uniquely prone to buying unhealthy food.
Moral Judgments: Food choices are often tied to morality in U.S. culture. People project ideas of “deservingness” onto what low-income families eat.
Simplification: It’s easier to blame individuals’ choices than to address systemic issues like food deserts, low wages, and the high cost of fresh produce.🌱 The Bigger Picture
The stereotype distracts from the real problem: structural barriers to healthy eating. Many SNAP households live in areas with limited access to affordable fresh food, and SNAP benefits often run out before the end of the month. The issue isn’t that people “only buy junk food”—it’s that the system doesn’t always make healthier options accessible or affordable.👉 In short, the “junk food SNAP user” is more myth than fact. It’s a narrative shaped by stigma, politics, and selective storytelling, not by the everyday reality of families stretching their benefits to cover basic groceries.
Virginia Giuffre’s memoir, Nobody’s Girl: A Memoir of Surviving Abuse and Fighting for Justice, is her posthumous account of being groomed and trafficked as a teenager by Jeffrey Epstein and Ghislaine Maxwell, her encounters with powerful men, and her long fight to reclaim her voice and seek justice.---### 📖 Core Themes of the Memoir
- Exploitation and Grooming: Giuffre describes how, at just 16, she was lured into Epstein’s orbit under the guise of training as a massage therapist. What followed was a system of psychological manipulation where “obedience was praised, disobedience punished”.
- High-Profile Connections: The book recounts her experiences being trafficked to influential men, including allegations against Prince Andrew, and mentions encounters with figures such as Bill Clinton and Donald Trump (though not alleging crimes against them).
- Breaking Down Defenses: She explains how Epstein and Maxwell “step by practiced step” eroded her sense of self, using fear, control, and normalization of abuse.
- Trauma and Survival: Beyond the salacious headlines, Giuffre emphasizes the lasting psychological toll of abuse and her struggle to move beyond being defined solely as “an Epstein victim”.
- Justice and Advocacy: The memoir highlights her determination to hold abusers accountable, her legal battles, and her advocacy for stronger protections for survivors of sexual exploitation.---### 🧩 Structure and Impact
- Title & Publication: Nobody’s Girl was co-written with journalist Amy Wallace and published in October 2025, six months after Giuffre’s death at age 41.
- Tone: The narrative blends personal testimony with investigative detail, exposing how systemic power and wealth shielded predators.
- Cultural Significance: The memoir has been described as both a personal emancipation and a public reckoning, accelerating scrutiny of Epstein’s network and contributing to Prince Andrew’s permanent removal from royal duties.---### ⚖️ Why It Matters
Giuffre’s story is not just about her own suffering—it’s about how systems of privilege and silence enable abuse. By publishing her memoir, she sought to ensure her voice could not be erased, even after her death. Friends and collaborators have said she hoped the book would free her from having to retell her trauma repeatedly, allowing her legacy to focus on advocacy and change.---👉 In short: Nobody’s Girl is both a harrowing survival story and a call to action, exposing how power, wealth, and silence perpetuate abuse—and how one survivor fought to reclaim her narrative.
Quick Answer:
Preservative-free eye drops are gentler on the eyes and better for frequent or sensitive use, while preservative-containing drops are more cost-effective and convenient for occasional use. Which is “better” depends on your eye health, sensitivity, and how often you need them.---### 🧴 Preservative-Containing Eye Drops
- What they are: Multi-use bottles with added chemicals (commonly benzalkonium chloride, or BAK) to prevent bacterial growth.
- Advantages:
- Longer shelf life
- More affordable and convenient (one bottle lasts weeks to months)
- Easy to carry and use multiple times without worrying about contamination
- Drawbacks:
- Preservatives can irritate the eye surface, especially with frequent use
- May worsen dryness, redness, or allergic reactions in sensitive individuals
- Long-term use can damage the corneal surface in some people---### 🌿 Preservative-Free Eye Drops
- What they are: Single-use vials or special multi-dose bottles designed to stay sterile without preservatives.
- Advantages:
- Gentle on the eyes—ideal for sensitive eyes, contact lens wearers, or post-surgery recovery
- Can be used as often as needed without risk of preservative toxicity
- Reduce the risk of allergic reactions or worsening dryness
- Drawbacks:
- More expensive
- Shorter shelf life once opened (often 24 hours for vials, ~3 months for special bottles)
- Less convenient to carry around if using single-use vials---### ⚖️ Which Is Better?
- Occasional users with no sensitivity: Preserved drops are usually fine, cost-effective, and convenient.
- Frequent users (more than 4 times/day), sensitive eyes, or post-surgery: Preservative-free drops are strongly recommended, as they avoid irritation and long-term damage.
- Contact lens wearers: Preservative-free is generally safer, since preservatives can bind to lenses and cause irritation.---### ✅ Bottom Line
- Preservative-free = safer for frequent, sensitive, or long-term use.
- Preserved = practical for occasional, short-term relief.
- The “best” choice depends on your personal eye health and usage pattern. If you’re unsure, an optometrist or ophthalmologist can guide you to the right option for your situation.
Yes — some memory changes are a normal part of aging. As we grow older, it’s common to notice slower recall, occasional forgetfulness, or needing reminders more often. However, significant or disruptive memory loss is not considered a normal part of aging and may signal something more serious.---### 🧠 What’s Normal with Age
- Slower recall: It may take longer to remember names, words, or details, but they usually come back with time or a hint.
- Occasional forgetfulness: Misplacing keys, forgetting an appointment, or needing lists is common.
- Learning curve: Picking up new skills or information may take longer, but older adults often excel at seeing “the big picture” and connecting ideas.### 🚩 When It May Be More Than Aging
According to the National Institute on Aging and Mayo Clinic:
- Asking the same questions repeatedly
- Getting lost in familiar places
- Difficulty following directions or recipes
- Forgetting common words or substituting unusual ones
- Misplacing items in odd places (like putting keys in the fridge)
- Struggling with daily tasks or self-careThese may point to mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or dementia-related conditions, which are not part of normal aging.### 🌱 Factors That Can Affect Memory
Not all memory issues are due to aging. Other causes include:
- Stress, anxiety, or depression
- Poor sleep or untreated sleep apnea
- Medication side effects
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Thyroid or other medical conditions
- Alcohol useMany of these are treatable, so it’s worth checking with a doctor if memory changes feel unusual or disruptive.### 🛠️ Tips to Support Memory
- Keep a routine and use tools like calendars or notes
- Place essentials (keys, glasses, phone) in the same spot daily
- Stay physically active and eat a balanced diet
- Get 7–8 hours of sleep each night
- Stay socially engaged with friends, family, or community groups
- Challenge your brain with new skills, puzzles, or hobbies---✅ Bottom line: Mild forgetfulness is normal as we age, but persistent or disruptive memory problems should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
Yes—quitting smoking does help reduce dementia risk. Research shows that smoking increases the likelihood of developing Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia, while stopping smoking lowers that risk, sometimes to the level of non-smokers. Even quitting later in life can slow memory decline and protect brain health.---### 🔑 Key Points
- Smoking raises dementia risk: Cigarette smoke damages blood vessels, increases inflammation, and stresses brain cells. These effects are strongly linked to both Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia.
- Quitting reduces risk: Studies show that people who stop smoking have a 30–50% lower risk of dementia compared to those who continue. Over time, ex-smokers’ risk can approach that of people who never smoked.
- Benefits at any age: Even quitting after age 50 is associated with slower memory decline (20% slower) and better verbal fluency (50% slower decline) compared to those who keep smoking.
- Cognitive health improves: Quitting helps preserve memory, focus, and problem-solving abilities. Within about 10 years, the risk of Alzheimer’s disease for ex-smokers can become similar to never-smokers.
- Second-hand smoke matters too: Exposure to passive smoke also increases dementia risk, so reducing overall smoke exposure is important.---### 🧠 Why Quitting Helps the Brain
- Better blood flow: Smoking damages blood vessels, which increases stroke and vascular dementia risk. Quitting restores healthier circulation.
- Less inflammation: Cigarette toxins trigger chronic inflammation, a known contributor to Alzheimer’s disease.
- Slower cognitive decline: Studies show quitting slows the rate of memory and language decline, which are early signs of dementia progression.---### 🚀 Practical Takeaways
- It’s never too late to quit. Even older adults benefit from stopping, both for brain and overall health.
- Support helps: Nicotine replacement (patches, gum, lozenges, sprays) and counseling improve success rates.
- Think “heart and brain together.” What’s good for your cardiovascular system—like quitting smoking, exercising, and eating well—is also good for your brain.---✅ Bottom line: Quitting smoking is one of the most effective lifestyle changes you can make to protect your brain and reduce dementia risk. The earlier you quit, the greater the benefit—but even later in life, it’s absolutely worthwhile.
Short answer: Yes, adding Epsom salt (magnesium sulfate) to kitty litter can be harmful. Cats may lick their paws after using the litter, and ingesting Epsom salt can cause digestive upset, toxicity, or skin irritation. It’s not recommended as a litter additive.---### Why Epsom Salt Is Risky for Cats
- Ingestion risk: Cats groom themselves constantly. If Epsom salt sticks to their paws or fur, they may ingest it. Even small amounts can cause vomiting, diarrhea, or abdominal pain.
- Toxicity in larger amounts: Ingesting too much magnesium sulfate can lead to serious health issues like lethargy, weakness, or even more severe complications.
- Skin irritation: Some cats develop redness, itching, or discomfort if their paws or skin come into contact with Epsom salt.
- No litter benefits: Epsom salt doesn’t neutralize odor or clump waste like proper litter additives. It offers no real advantage in a litter box setting.---### Safer Alternatives for Litter Boxes
If your goal is odor control or sanitation, here are cat-safe options instead of Epsom salt:
- Baking soda (in moderation): A light sprinkle under the litter layer can help with odor without harming cats.
- Activated charcoal filters: Many litter boxes come with these to absorb smells.
- Unscented clumping litter: Designed specifically for cats, it’s the safest and most effective option.
- Frequent cleaning: Scooping daily and washing the box weekly with mild soap and water is the most reliable way to keep things fresh.---### Bottom Line
Don’t add Epsom salt to kitty litter. While it’s safe for humans in baths, it poses unnecessary risks for cats. Stick with cat-safe litter products and cleaning practices to protect your pet’s health.
Quick Answer: Yes, adult cats can eat kitten food occasionally without harm, but it’s not ideal as their main diet. Kitten food is higher in protein, fat, and calories, which can lead to weight gain and nutritional imbalance in adult cats if fed long-term.---### 🐾 Why Kitten Food Exists
- Formulated for growth: Kitten food is designed to fuel rapid development, with extra protein, fat, and calories to support bone, muscle, and brain growth.
- Nutrient-dense: It often contains higher levels of certain vitamins and minerals, like calcium and phosphorus, which kittens need more of than adults.### 🐱 Adult Cats Eating Kitten Food
- Safe short-term: If you run out of adult cat food, feeding kitten food for a few days is fine. It won’t harm your cat in the short run.
- Not ideal long-term: Adult cats don’t need the same calorie load. Over time, eating kitten food can cause weight gain, obesity, and digestive upset.
- Exceptions:
- Pregnant or nursing cats benefit from kitten food because of the higher calorie and nutrient density.
- Underweight or recovering cats may also be prescribed kitten food temporarily by a vet.### ⚖️ Key Differences Between Adult & Kitten Food| Feature | Kitten Food 🍼 | Adult Cat Food 🐾 |
|----------------------|----------------|------------------|
| Protein | Higher | Moderate |
| Fat & Calories | Higher | Balanced |
| Calcium/Phosphorus | Higher | Lower |
| Intended Use | Growth & development | Maintenance & weight control |### ✅ Best Practice
- Feed adult cats adult food for balanced nutrition.
- Use kitten food only as a temporary substitute or under veterinary guidance.
- If your cat sneaks a few bites of kitten food, don’t worry—it’s safe in moderation.---
Quick answer: Papayas are generally considered a medium glycemic index (GI) fruit but with a low glycemic load (GL). This means they don’t cause sharp spikes in blood sugar when eaten in moderate portions.---### 🍈 Glycemic Index (GI) of Papaya
- The glycemic index measures how quickly a food raises blood sugar compared to pure glucose.
- Papaya’s GI values vary depending on ripeness and preparation:
- Some studies report a low GI around 38–42 for raw papaya.
- Others classify it as medium GI, around 55–60.
- On average, papaya is best described as low-to-medium GI.### 📊 Glycemic Load (GL) of Papaya
- Glycemic load accounts for both the GI and the amount of carbohydrate in a typical serving.
- For papaya:
- GL ≈ 5.5 per 100 g → this is considered low.
- This means that even though papaya has natural sugars, the overall effect on blood sugar is modest when eaten in reasonable amounts.### 🥭 Why Papaya Can Be a Good Choice
- Rich in fiber → slows sugar absorption.
- High in vitamin C, antioxidants, and magnesium → supports overall metabolic health.
- Low calorie density → about 48 kcal per 100 g.
- May help with digestion and inflammation, which are linked to better blood sugar control.### ✅ Practical Takeaway
- Papayas are not “high glycemic” fruits. They fall into the medium GI range but with a low GL, making them a safe and nutritious option for most people, including those managing blood sugar.
- Portion size still matters: a small bowl (about 100–150 g) is a balanced serving.
Short answer: When people say “Thanos was right,” they mean that his core concern—overpopulation and resource scarcity—had some truth to it, even if his solution (erasing half of all life) was horrific and deeply flawed. It’s become a cultural shorthand for the idea that he identified a real problem, but chose the worst possible way to address it.---### 🌌 Breaking it down
- Thanos’ belief: In Avengers: Infinity War, Thanos argued that the universe was suffering from overpopulation and dwindling resources. His “solution” was to wipe out half of all life instantly, believing this would restore balance and prosperity.
- The Snap: Using the Infinity Gauntlet, he carried out this plan—what fans call “The Snap”—erasing 50% of all living beings.
- Why some say he was “right”:
- He correctly identified that unchecked growth and consumption can lead to collapse.
- In the MCU, some survivors even admitted life briefly felt “better” after the Snap—less crowded, more resources available.
- Why he was wrong:
- Genocide is not a solution. His method was mass murder on a cosmic scale.
- It’s a temporary fix—populations would rebound, and the same issues would return.
- He ignored alternatives like sharing knowledge, expanding into new worlds, or creating more resources (which the Infinity Stones could arguably do).---### 🧩 In the MCU itself
- In Hawkeye and The Falcon and the Winter Soldier, graffiti, mugs, and slogans reading “Thanos Was Right” appear, showing that some ordinary people in-universe sympathized with his logic.
- In Eternals, Marvel even hinted that his actions may have delayed a catastrophic event, adding fuel to the debate.---### 💡 Why the phrase stuck in pop culture
- It’s become a meme and discussion starter: a way to talk about real-world issues like climate change, inequality, and sustainability.
- It reflects the appeal of villains who are “wrong in execution but right in diagnosis.” Like Killmonger in Black Panther, Thanos resonates because his motives touch on real anxieties.---👉 So when you hear “Thanos was right,” it’s less about endorsing his genocide and more about acknowledging that he raised a valid concern—just in the most monstrous way possible.
Yes — the No Kings Day protest on June 14, 2025, was one of the largest single-day demonstrations in U.S. history, with over five million participants across more than 2,100 locations nationwide. Analysts rank it as likely the second-largest protest day since the Women’s March of January 2017.---### 📊 Key Facts About No Kings Day
- Date: June 14, 2025
- Scale: More than 5 million protesters participated across 2,100+ cities and towns in the U.S.
- Geographic spread: Demonstrations occurred in nearly every state, plus solidarity events abroad.
- Cause: Opposition to democratic backsliding and authoritarian tendencies during Donald Trump’s second administration.
- Organizers: A coalition including the 50501 movement, Indivisible, MoveOn, and other grassroots groups.### 🔎 How It Compares Historically
- Women’s March (Jan. 21, 2017): Estimated 5–7 million participants worldwide, making it the largest single-day protest in U.S. history.
- No Kings Day (June 14, 2025): Ranked just behind the Women’s March, but ahead of most other major protest days in terms of turnout.
- Other large protests for context:
- George Floyd protests (2020) were massive but spread over weeks, not a single day.
- March for Our Lives (2018) drew hundreds of thousands, but not millions.### 🌍 Why It Stood Out
- Nationwide coordination: The protests weren’t confined to major cities — small towns and rural areas also saw significant turnout.
- Symbolism: The name “No Kings” emphasized resistance to authoritarianism and the rejection of concentrated executive power.
- Durability: Analysts noted that the scale and breadth of participation signaled a sustained pro-democracy movement, not just a one-off event.---✅ In short: No Kings Day was indeed one of the largest protest days in U.S. history — second only to the Women’s March — and it demonstrated both the depth and breadth of opposition to Trump’s second administration.
Quick Answer: The so‑called “Qatar air base” in Idaho is not a separate foreign base at all. It’s a new training and maintenance facility for Qatari pilots and F‑15QA fighter jets being built at Mountain Home Air Force Base, southeast of Boise. The base remains fully under U.S. Air Force control; Qatar is funding the construction as part of a long‑standing defense partnership.---### 📖 The Background
- Location: Mountain Home Air Force Base, about 50 miles southeast of Boise, Idaho. It’s known as the “Gunfighter” base and houses the 366th Fighter Wing with more than 50 F‑15E Strike Eagles.
- Why Idaho? The high desert plateau offers wide‑open airspace, ideal for fighter pilot training. The base already hosts foreign partners, such as the Singaporean Air Force’s 428th Fighter Squadron since 2008.### ✈️ The Qatar Agreement
- Aircraft involved: Qatar purchased the F‑15QA, a specialized version of the F‑15, through U.S. foreign military sales.
- Purpose of the facility: To provide squadron operations buildings, hangars, and training infrastructure for Qatari pilots and crews.
- Funding: The Qatari government is paying for construction and related expenses, but the facility is on U.S. soil and under U.S. security control.
- Security: All access remains governed by U.S. Air Force personnel. Qataris will train there, but they do not “own” or control the base.### 🌍 Broader Context
- Not unusual: The U.S. has a history of hosting allied forces for training. Examples include:
- German pilots at Holloman AFB in New Mexico (for decades).
- Singaporean pilots at Mountain Home since 2008.
- International F‑35 training at Ebbing AFB in Arkansas.
- Strategic partnership: Qatar already hosts the Al Udeid Air Base, the largest U.S. military installation in the Middle East. The Idaho facility strengthens interoperability and joint readiness between the two nations.### ⚡ Public Reaction
- The announcement in October 2025 sparked confusion and controversy online, with some claiming the U.S. was allowing a foreign military base on American soil.
- Officials clarified repeatedly: this is not a foreign base, but a U.S. base with a Qatari training presence, similar to other allied arrangements.---✅ In short: The “Qatar air base in Idaho” is really a Qatari‑funded training facility at a U.S. Air Force base, designed to support their new F‑15QA jets. It’s part of a broader U.S.–Qatar defense partnership, and the base remains entirely under U.S. control.
Cats scratch furniture and shred toilet paper because it's instinctual, stimulating, and satisfying — behaviors rooted in play, territory marking, and stress relief. These actions mimic hunting and help cats maintain their claws, stretch muscles, and express emotions.---### 🐾 Why Cats Scratch Furniture- Territory Marking: Cats have scent glands in their paw pads. Scratching leaves both visual and olfactory marks, signaling ownership to other animals.
- Claw Maintenance: Scratching removes the outer sheath of claws, keeping them sharp and healthy.
- Stretching & Exercise: It’s a full-body stretch that helps relieve muscle tension and maintain flexibility.
- Stress Relief: Scratching releases calming chemicals in the brain, helping cats manage anxiety or excitement.
- Preference for Vertical Surfaces: Cats often target couch arms or wooden furniture because they mimic tree trunks — ideal for marking territory at eye level.---### 🧻 Why Cats Shred Toilet Paper- Play & Curiosity: Toilet paper is light, crinkly, and easy to tear — perfect for mimicking prey. Cats enjoy the tactile and auditory feedback.
- Hunting Simulation: Shredding resembles a successful hunt. The paper’s destruction signals a “kill,” satisfying their natural instincts.
- Boredom: Without enough stimulation, cats may turn to toilet paper for entertainment. It’s a sign they need more toys or interactive play.
- Territorial Behavior: Like furniture, toilet paper can be scratched to leave scent marks.
- Texture & Sound: Some cats simply enjoy the feel and noise of tearing paper — similar to humans popping bubble wrap.---### 🛠️ How to Redirect These Behaviors- Provide scratching posts (vertical and horizontal) in key areas.
- Use interactive toys and puzzle feeders to reduce boredom.
- Try double-sided tape or deterrent sprays on furniture.
- Keep toilet paper out of reach or use covered dispensers.
- Reward your cat when they use appropriate outlets.---
Dirty soda is a non-alcoholic drink trend that started in Utah and has since spread across the U.S. It’s basically a regular soda that’s been “dressed up” with flavored syrups, fruit juices, cream, or coconut milk—kind of like a soda-based mocktail.### 🍹 What Makes It “Dirty”
- Base soda: Usually Coke, Diet Coke, Dr Pepper, Sprite, or root beer.
- Flavor add-ins: Coconut, vanilla, raspberry, passionfruit, or other syrups.
- Creamy twist: Half-and-half, heavy cream, or coconut cream.
- Extras: Fresh lime, fruit purées, or even seasonal spices.For example:
- Dirty Dr Pepper → Dr Pepper + coconut syrup
- The Original Dirty Soda → Diet Coke + coconut syrup + lime + cream
- Island Time (from Swig, a popular soda shop) → Fresca + passionfruit syrup + mango purée + coconut cream### 🌟 Origins & Popularity
- The drink became popular in Utah’s Mormon community as a fun alternative to coffee, tea, or alcohol, which are avoided for religious reasons.
- The first official “dirty soda” shop, Swig, opened in 2010 in St. George, Utah.
- It blew up on TikTok and Instagram after celebrities like Olivia Rodrigo were spotted with it, making it a nationwide trend.### 🥤 The Vibe
Think of dirty soda as the Starbucks of soda—customizable, indulgent, and often served in giant cups with pebble ice. It’s sweet, creamy, and a little over-the-top, which is exactly why people love it.
Great question—this one sits right at the crossroads of biology, psychology, and sociology. The short answer is: stress is both biological and socially constructed. Let me break it down:### 🧠 The Biological Reality
- Stress has a clear physiological basis. When you perceive a threat, your body releases hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. This “fight-or-flight” response is measurable and universal across humans (and even animals).
- So in that sense, stress is not just a social construct—it has real, physical consequences.### 🌍 The Social Construction Side
- Sociologists argue that what counts as “stressful” is shaped by culture, history, and social structures. For example:
- In pre-industrial societies, stress was often tied to survival threats (famine, predators).
- In industrial and post-industrial societies, stress shifted toward work deadlines, financial insecurity, or social expectations.
- Social class, gender, race, and cultural norms all influence how stress is experienced and expressed. For instance, what one culture sees as a stressful burden, another might see as a normal rite of passage.
- Researchers even debate whether “stress” as a category is partly a modern invention—popularized by medicine, psychology, and media in the 20th century.### ⚖️ Putting It Together
- Stress is real in the body, but the meaning, triggers, and coping strategies are socially constructed.
- Think of it like pain: the nerves fire in everyone, but how we interpret, express, and treat pain depends heavily on culture and context.👉 So, stress isn’t only a social construct, but our understanding of it—and the way it shapes our lives—is deeply social.
Many cat owners push back against carrageenan in pet food because of concerns over its potential health effects, even though it’s a common, plant-derived thickener made from red seaweed. The opposition usually comes down to three main points:---### 🐾 1. Digestive Inflammation Concerns
- Some studies have linked carrageenan—especially in sensitive species—to intestinal inflammation and irritation.
- Cats have delicate digestive systems, so owners worry it could contribute to issues like vomiting, diarrhea, or flare-ups in conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).---### ⚠️ 2. Potential Breakdown into Harmful Compounds
- There are two forms:
- Food-grade (undegraded) carrageenan — approved for use in food.
- Degraded (poligeenan) — not approved for consumption due to its inflammatory and possibly carcinogenic effects.
- Some researchers suggest that in a cat’s highly acidic stomach, food-grade carrageenan might partially break down into poligeenan, raising safety concerns.---### 🩺 3. Vet & Consumer Caution
- While the FDA and some vets say regulated amounts are safe, others recommend avoiding it entirely—especially for cats with chronic digestive issues, food sensitivities, or compromised immune systems.
- This has fueled a market shift toward carrageenan-free wet foods, using alternatives like guar gum, agar-agar, or xanthan gum.---💡 Bottom line: The science is mixed—some studies find no harm, others raise red flags—but many cat owners choose to avoid carrageenan as a “better safe than sorry” move, especially when carrageenan-free options are easy to find.
Paradoxically, yes — “doing nothing” is still doing something, both philosophically and neurologically.Here’s why:### 🧠 From a brain science perspective
- Your brain never truly stops — even when you’re not engaged in a task, it switches to the default mode network (DMN), which handles memory consolidation, self-reflection, and creative problem-solving.
- This “idle” state is when your mind integrates experiences, makes unexpected connections, and recharges cognitive resources.### 🪷 From a philosophical angle
- Inaction can be a deliberate action. Choosing to rest, reflect, or simply “be” is still an intentional state of engagement with the present moment.
- Taoist and Zen traditions often frame “doing nothing” (wu wei) as a form of harmonious action — letting things unfold without force.### ⚡ From a productivity lens
- Pausing prevents burnout and can actually make you more effective later.
- Many breakthroughs happen during downtime — think of Archimedes in the bath or Einstein on a walk.In short: doing nothing is not the absence of action — it’s a different mode of action, one that works quietly in the background to restore, integrate, and create.
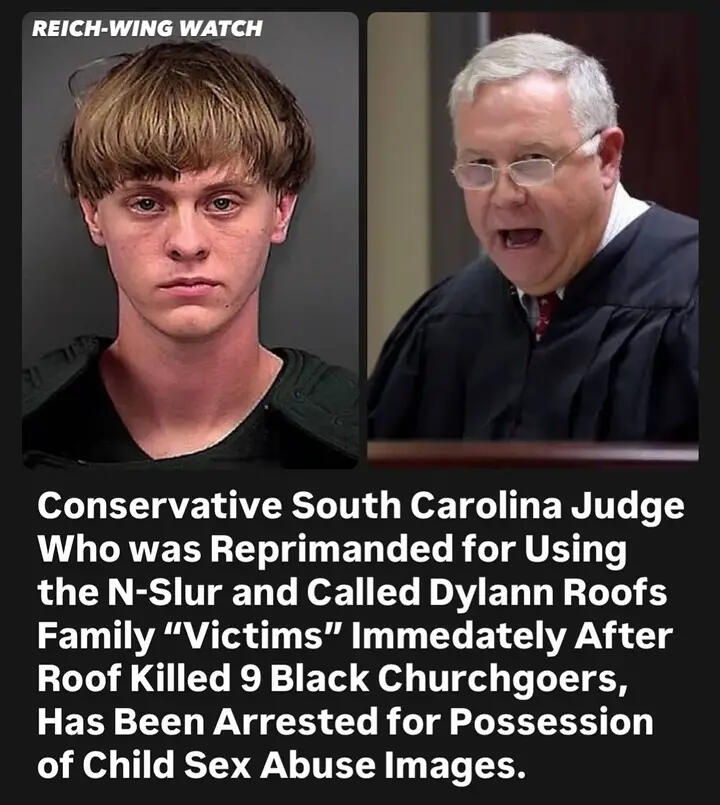
Yes — this one is real, and it’s been confirmed by multiple reputable outlets.The man in the meme is James B. Gosnell Jr., a longtime Charleston County, South Carolina magistrate judge. Here’s what’s been verified:- Arrest & Charges (2025) – Gosnell was arrested in September 2025 on federal charges of possessing child sexual abuse material. Homeland Security Investigations traced payments from his accounts to a known distributor in the UK, and a search of his home uncovered a flash drive containing numerous explicit images and videos of minors, including infants.
- Past Controversies – Gosnell presided over the 2015 bond hearing for mass shooter Dylann Roof and drew criticism for saying Roof’s family were also “victims”.
- Racist Remarks – In 2003, he used a racial slur in court, leading to a formal reprimand by the South Carolina Supreme Court.So the meme’s core claims — that he was reprimanded for racist remarks, made the “victims” comment about Roof’s family, and has now been arrested on child sexual abuse material charges — are supported by credible reporting.
Absolutely — sunflower seeds are a nutrient-dense snack with some impressive health perks when eaten in moderation.Here’s a quick breakdown of why they’re considered good for you:### 🌻 Key Nutrients
- Healthy fats – Rich in polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats that support heart health
- Protein – Helps with muscle repair and satiety
- Vitamin E – A powerful antioxidant that protects cells from damage and supports skin health
- Magnesium – Important for muscle function, nerve health, and energy production
- Zinc & Selenium – Support immune function and help reduce inflammation### 💪 Potential Health Benefits
- Heart health – May help lower blood pressure, cholesterol, and risk of cardiovascular disease
- Anti-inflammatory effects – Thanks to vitamin E, flavonoids, and plant compounds
- Blood sugar balance – Can help stabilize glucose levels
- Cancer-protective properties – High in antioxidants and conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), which may help prevent certain cancers
- Thyroid support – Nutrients like selenium contribute to healthy thyroid function### ⚖️ Things to Keep in Mind
- Portion control – They’re calorie-dense, so a small handful (about 1 oz / 28 g) is a good serving.
- Sodium – Opt for unsalted or lightly salted varieties to avoid excess salt.
- Added oils – Check labels if buying flavored or roasted seeds.
Not really — in fact, overcooking sliced potatoes is more likely to reduce their resistant starch rather than increase it.Here’s why:### 🔬 The science of resistant starch in potatoes
- Resistant starch (RS) is starch that escapes digestion in the small intestine and feeds your gut bacteria in the large intestine.
- In potatoes, the main type you can influence is RS3 (retrograded starch), which forms when cooked starches cool down and recrystallize.
- The best way to boost RS in potatoes is the cook → cool → (optional) reheat cycle — for example, boiling or baking, chilling in the fridge for several hours, then eating cold or gently reheated.### 🍳 What overcooking does
- When you overcook potatoes (especially slices), the starch granules gelatinize fully and the cell walls break down.
- Prolonged heat can cause excessive gelatinization and moisture loss, which doesn’t create more RS — it actually makes the starch more digestible in the moment.
- RS3 only forms after cooling, not during extended cooking.
- Overcooking can also lead to retrogradation in a negative way — the texture may harden if cooled, but that’s not the same as a big RS boost, and much of the starch may already be broken down.### ✅ Best method to increase resistant starch in potato slices
1. Cook until just tender (boiling, steaming, or baking).
2. Cool completely in the fridge for at least 8–12 hours.
3. Eat cold (e.g., in a potato salad) or reheat gently — RS3 survives mild reheating.💡 Fun fact: Cooling can increase resistant starch in potatoes by roughly 50–60% compared to eating them hot, but the absolute amount is still modest.
Yes — research suggests creatine can help lower blood sugar, especially when paired with regular exercise, though it’s not a direct blood sugar–lowering supplement like medication.Here’s the breakdown:### 🧬 How it works
- Boosts glucose uptake into muscles – Creatine appears to enhance the activity of GLUT-4 transporters, which move glucose from your blood into muscle cells.
- Improves insulin sensitivity – By making muscles more efficient at using glucose during and after exercise, creatine may help your body respond better to insulin.
- Supports muscle growth – More muscle mass means more tissue available to store glucose, which can help stabilize blood sugar over time.### 📊 What studies show
- In people with type 2 diabetes, a 12‑week program combining creatine with exercise improved glycemic control and reduced HbA1c levels.
- Healthy individuals have also shown better glucose tolerance after creatine use, particularly during exercise.
- The effect is most pronounced in those with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes, and less noticeable in people with normal glucose metabolism.### ⚠️ Things to keep in mind
- Creatine itself doesn’t spike blood sugar — but mixing it with sugary drinks will.
- Some people notice small, temporary changes in readings when starting creatine, often due to hydration shifts rather than glucose effects.
- If you have diabetes or prediabetes, it’s wise to monitor your blood sugar more closely during the first week or two of supplementation.
They’re related, but not identical — think of free choice as the visible action and free will as the underlying capacity that makes that action possible.Here’s the breakdown:| Concept | What it Means | Scope | Key Point |
|---------|--------------|-------|-----------|
| Free Choice | The act of selecting between two or more available options | Narrow — limited to the options in front of you | You can choose chocolate or vanilla, but only from what’s offered |
| Free Will | The ability to make decisions that are not wholly determined by external forces or past events | Broad — includes the capacity to form intentions, values, and desires | It’s the power to decide in the first place, even shaping what options exist for you |In short:
- Free choice is the expression of free will in a specific moment.
- Free will is the capacity to make choices at all, ideally without coercion or total determinism.
- You can have free choice without full free will — for example, if your available options are heavily constrained by outside forces.Philosophers often debate whether we truly have free will (especially in light of determinism), but most agree that free choice is just one manifestation of it.
Yes — white vinegar can help neutralize urine odor, but it works best in certain situations and with the right method.Here’s why and how:### 🧪 Why it works
- Chemical reaction – Urine odor often comes from ammonia and uric acid. Vinegar’s acidity can react with these alkaline compounds, reducing their volatility and smell.
- Natural deodorizer – It’s a safer, non-toxic alternative to harsh chemical cleaners, especially for households with kids or pets.### 🛠 How to use it effectively
1. Dilute first – Mix equal parts white vinegar and water to avoid damaging fabrics or carpet fibers.
2. Apply generously – Spray or pour onto the affected area so it penetrates where the urine has soaked in.
3. Let it sit – Wait 5–15 minutes to allow the vinegar to break down odor-causing compounds.
4. Blot, don’t rub – Press with a clean towel to absorb moisture without pushing it deeper.
5. Optional boost – After it dries, sprinkle baking soda over the spot to absorb any lingering smell, then vacuum.### ⚠️ Things to keep in mind
- For pet urine – Vinegar’s strong scent can sometimes encourage pets to re-mark the area. In that case, an enzymatic cleaner is more effective because it breaks down uric acid completely.
- Test first – Always spot-test on fabrics or carpet to ensure no discoloration.
- Not a magic eraser – Vinegar helps with odor, but deep-set stains or smells may need multiple treatments or specialized cleaners.
Cats nibbling on grass or leafy plants might look odd for an obligate carnivore, but it’s actually a well-documented and fairly common behavior — and it’s not always a sign something’s wrong.
Here are the leading science-backed theories for why they do it:🌿 Hairball & Indigestible Material Purge
- Grass can trigger vomiting, which may help cats expel fur, feathers, or tiny bone fragments from prey (or just hairballs from grooming).🚽 Mild Constipation Relief
- If the grass isn’t vomited up, it often passes through unchanged, adding roughage that can help move stool along.🛡 Ancient Parasite Defense
- In wild species, plant fibers can help sweep intestinal parasites out. Domestic cats may have inherited this instinct, even if they’re parasite-free.💊 Possible Nutrient Boost
- While cats can’t digest grass well, it may contain trace vitamins or minerals that fill small dietary gaps — though a balanced cat food should already cover these.😋 They Just Like It
- Some cats simply enjoy the taste or texture of grass and greens. It’s part curiosity, part preference.⚠ A Note on Safety
- Grass itself is usually fine, but many houseplants are toxic to cats. If your cat likes greens, offer pet-safe grass (like wheatgrass) and keep harmful plants out of reach.
Yes — the mango (Mangifera indica L.), specifically the Carabao mango, is officially recognized as the national fruit of the Philippines.
It’s not just a title for show — the mango is deeply woven into Filipino culture, cuisine, and economy:
🥭 Cultural Symbol – Seen as a sign of prosperity and happiness, and often featured in art, literature, and festivals like the Zambales Mango Festival.
🍰 Culinary Star – Used in everything from desserts like mango float and ice cream to savory dishes like mango salsa.
🌱 Economic Importance – Grown by millions of farmers, with the Carabao variety famous worldwide for its sweetness.
Fun fact: The Guinness World Records once listed the Carabao mango as the sweetest mango variety on Earth — a pretty sweet national emblem indeed.
Chuck Norris has generally maintained a wholesome, tough‑guy public image, but over the decades there have been a few controversies and disputes linked to his name — some personal, some legal, and some political. Here are some notable examples:---### 🪖 Early Military Service Dispute
- Air Force Discharge Debate – Norris served in the U.S. Air Force from 1958 to 1962, but his exit was clouded by reports of disciplinary issues. Accounts mention an AWOL incident, clashes with a drill sergeant, and being deemed unfit for officer training.
- In his autobiography, Norris claimed he was treated unfairly and singled out for harsh punishment, while others have argued his rebellious streak justified the discharge. A later academic review suggested he may have been punished more severely than peers.---### ⚖️ Gadolinium Lawsuit
- In 2017, Norris and his wife, Gena, sued several medical manufacturers, claiming she suffered serious health problems after being injected with gadolinium-based contrast agents during MRI scans.
- They sought $10 million in damages, alleging the substance “poisoned” her. The case drew attention to ongoing debates about gadolinium safety.
- In 2020, they voluntarily dropped the lawsuit without a settlement, with each side covering its own legal costs.---### 📹 Altered Political Video
- In 2022, a video circulated online appearing to show Norris warning that “freedom is under attack” and criticizing the Biden administration.
- Fact-checkers found the clip had been altered from its original context, sparking discussion about misinformation and the use of celebrity likeness in political messaging.---### 🗳 Political Endorsements & Backlash
- Norris has been outspoken in U.S. politics, endorsing conservative candidates and causes. While not a “scandal” in the legal sense, his political stances — including strong support for certain Republican figures — have occasionally drawn criticism from opponents and media commentators.---
Visceral has two main shades of meaning, one rooted in anatomy and the other in emotion:- 🫀 Literal (biological) – Relating to the viscera, which are the large internal organs inside your body, especially in the chest and abdomen (like the heart, lungs, stomach, and intestines). For example: “Visceral fat” refers to fat stored around these organs.
- 💥 Figurative (emotional) – Describing something felt deeply and instinctively, as if in your gut, rather than through logical thought. It’s often used for strong, raw, or primal reactions, like “a visceral fear of heights” or “a visceral thrill”.Synonyms (emotional sense): instinctive, gut-level, deep-seated, innate.
Example: Her visceral reaction to the news left her speechless.
Baking soda is the clear winner for odor absorption.Here’s why:
- Chemical makeup 🧪 — Baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) is mildly alkaline (pH ~8.3), so it reacts with and neutralizes many acidic odor molecules.
- How it works — When exposed to air, it interacts with odor-causing compounds, changing their pH and reducing their smell.
- Best uses — Sprinkle it on carpets, upholstery, or inside shoes; place an open box in the fridge or closet; or make a paste for surfaces. It usually needs at least 24 hours to work, and stubborn smells may take a few days.Baking powder, on the other hand, contains baking soda plus an acid (like cream of tartar), giving it a more neutral pH. That makes it far less effective at neutralizing odors, though it can still be used for gentle cleaning.
Glutamate is a fascinating multitasker in your body — it’s both:### 🧠 A Key Brain Messenger
- Most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in your brain.
- Sends signals between nerve cells, helping them “fire” and pass messages along.
- Crucial for learning, memory, mood regulation, and sleep cycles.
- Also needed to make GABA, the brain’s main calming neurotransmitter.### 💪 An Amino Acid
- One of the building blocks of proteins — your body’s most abundant amino acid.
- Found naturally in many foods (meats, mushrooms, soy, tomatoes) and also in the flavor enhancer monosodium glutamate (MSG).
- Your body can make it on its own, so it’s considered “non-essential” in the diet.### ⚖️ Balance Matters
- Too much glutamate in the brain can overstimulate nerve cells and is linked to conditions like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and certain mood disorders.
- Too little can impair energy supply to brain cells and affect cognitive function.
- Your nervous system tightly regulates glutamate levels to keep things in the healthy range.
# What Is a Calico Cat?## OverviewA calico cat is not a specific breed but a domestic cat distinguished by a three-color coat pattern: predominantly white patches alongside orange (red) and black markings.## Coat Patterns and Colors- White areas result from a gene that prevents pigment in certain parts of the fur.
- The orange and black patches arise from pigments produced by distinct alleles on the X chromosome.
- Each calico’s pattern is unique, ranging from large, blocky patches to fine, intermingled speckles.## Genetic BasisThe calico pattern is caused by X chromosome inactivation in female cats. Embryonic cells randomly switch off one of the two X chromosomes, leading to some cells producing orange pigment and others producing black. White fur appears where neither pigment gene is active.## Gender and Genetics- Almost all calico cats are female because they need two X chromosomes to display both orange and black fur.
- Male calicos are extremely rare and typically arise from a genetic anomaly such as Klinefelter syndrome (XXY), often resulting in sterility.## Variations of Calico Coats- Dilute calico: softer hues of cream, blue-gray, and pale apricot.
- Caliby (tabico): combines calico’s three colors with tabby striping within the orange or black areas.
- Tortoiseshell & white: sometimes called tricolor but with more mixed, brindled patches rather than clear block colors.---## Fun Facts You Might Enjoy- Calicos are sometimes called “money cats” in folklore, believed to bring good fortune.
- The term “calico” originally referred to a fabric printed with multicolored patterns.
- You’ll find calico coat patterns in many breeds, from the American Shorthair to the Japanese Bobtail.---
We habitually slap labels—success or failure—on life’s events, yet reality rarely fits those boxes. What feels like loss can spark new beginnings, and setbacks often teach resilience. The real work is learning to sit with uncertainty: letting go of our urge to define and control, and instead opening ourselves to life’s unfolding mystery. This isn’t blind optimism but a practice of patience and humility, shifting our focus from finding answers to embracing possibility.---Practical ways to live this out:- Pause before you judge: Notice the impulse to label an experience and give yourself a moment of openness instead.
- Keep an “unknowns” journal: Record situations you can’t explain, then revisit them later to see how they’ve shifted.
- Try beginner’s mind meditation: Focus on sensations or thoughts without naming or evaluating them.
- Cultivate curiosity questions: Ask “What might this teach me?” rather than “Why is this happening to me?”
- Lean on community: Share your uncertainties with friends—vulnerability dissolves the illusion of control.
# What Is Treated Wood?Treated wood is lumber that’s been infused with preservative chemicals to prolong its service life, especially in environments prone to moisture, decay fungi, insects, or other degrading factors. Unlike untreated wood, these chemicals penetrate beyond the surface, helping the wood resist rot and pest damage for decades rather than just a few years.## How It’s MadePressure-treated wood is produced by placing raw lumber inside a sealed chamber and using vacuum and high-pressure cycles to force waterborne or oil-borne preservatives deep into the wood fibers. This pressure-impregnation process ensures the protective chemicals remain even after cutting, drilling, or surface wear.---## Common Types of Treatments- Waterborne preservatives
- Oil-borne formulations
- Creosote (mostly for marine and railroad applications)
- Fire-retardant treatmentsEach type targets specific threats—fungal rot, termites, marine borers, or flame spread—and is chosen based on the intended end use and exposure conditions.---## Key Benefits and Uses- Extended lifespan: Treated wood can last 25 years or more versus 1–2 years for untreated lumber in harsh conditions
- Versatility: Ideal for decks, fence posts, playground equipment, and ground-contact applications
- Eco-impact: Fewer trees harvested over time, since treated pieces don’t need frequent replacement---## Standards and SafetyAll preservative chemicals used in treated wood are registered pesticides regulated by the U.S. EPA. The American Wood Protection Association (AWPA) sets use-category standards—clearly marked on each piece—to match preservative types and retention levels with specific exposure environments.---
# How Creatine Influences SleepCreatine isn’t just for gym gains—it also interacts with your sleep through several intriguing pathways. As more research emerges, understanding these effects can help you optimize both your supplementation strategy and your rest.---## Key Mechanisms1. Regulation of Mood
- Creatine supports synthesis of dopamine and serotonin, which not only boost mood but also play roles in sleep onset and maintenance.2. Modulation of Sleep Pressure
- By reducing accumulation of adenosine (the neuromodulator that builds up the longer you’re awake), creatine may lower the “sleep pressure” you feel, potentially reducing the need for deep, slow-wave sleep without sacrificing cognitive performance.3. Brain Energy Buffering
- Increased phosphocreatine stores in the brain help regenerate cellular energy more efficiently. This may translate into better sleep efficiency and less grogginess (sleep inertia) upon waking.4. Enhanced Sleep Duration After Exercise
- In resistance-trained women, supplementation extended total sleep time on training days compared to placebo, suggesting creatine can aid recovery by improving post-workout rest.---## Benefits for Sleep DeprivationWhen sleep is cut short, your brain’s energy reserves dwindle. Creatine may help counteract these deficits:- Cognitive Performance
Maintains alertness and mental function even after insufficient sleep.
- Reduced Fatigue
Boosts available energy, lessening tiredness associated with sleep loss.
- Improved Mood
Stabilizes mood swings that often accompany chronic sleep deprivation.---## Potential DrawbacksNot everyone experiences only upsides—some report challenges when supplementing with creatine:- Difficulty Falling or Staying Asleep
Heightened cellular energy and reduced sleep pressure might backfire for sensitive individuals, leading to insomnia-like symptoms.
- Individual Variability
Effects depend on dosage, timing (morning vs. evening), and personal physiology.Balancing these factors is key to harnessing creatine’s benefits without compromising rest.---## Practical Recommendations1. Timing Matters
- Morning or post-workout dosing may minimize nighttime stimulation.2. Start Low, Go Slow
- Begin with a smaller daily dose (2–3 g) before ramping up to the typical 5 g to gauge your sleep response.3. Monitor Sleep Metrics
- Use a sleep tracker or journal to note changes in sleep onset, duration, and quality.4. Combine with Good Sleep Hygiene
- Stick to consistent bedtimes, limit caffeine late in the day, and create a cool, dark bedroom environment.---## Beyond Creatine: Related Insights- Alternative Supplements: Magnesium, L-theanine, and tart cherry extract each have distinct sleep-promoting pathways.
- Dietary Factors: Carbohydrate timing and protein quality can also influence nighttime recovery.
- Chronotype Considerations: If you’re naturally a night owl or early bird, tailor your creatine schedule to align with your peak energy periods.
- Future Directions: Ongoing studies are examining how creatine interacts with other neuromodulators like GABA and glutamate, potentially offering new avenues for sleep support.
Taylor Swift’s “new era” is her way of signaling a distinct creative chapter tied to a forthcoming album. Each era comes with its own color palette, visual motifs, storytelling themes and marketing rollout. When Swift declares she’s entering a new era, she’s announcing that the next album cycle—with its music, videos, fashion and tour concept—is officially underway.She masterminds the reveal through layered Easter eggs: in August 2025, an orange-sparkle countdown appeared on her website set to expire at 12:12 a.m. ET, her in-house team posted a 12-photo carousel of orange tour outfits and then teased her debut on the New Heights podcast. At midnight on August 12, she opened a mint-green briefcase marked “T.S. 12” and unveiled The Life of a Showgirl—her 12th studio album and the kickoff of her newest era.For fans and the industry, a new era means more than just an album drop. It heralds new singles, music videos, merchandise, visual aesthetics (from stage design to clothing) and, often, a world-spanning tour. It’s a multi-month campaign that reshapes how we experience Taylor’s evolving artistry.---Additional insights you might want to explore:- How Swift’s eras have evolved: from the fairy-dust whimsy of Fearless (2008) through the midnight-blue melancholy of Midnights (2022) to the self-reflexive darkness of The Tortured Poets Department (2024).
- The symbolic role of color in Swift’s storytelling—why orange (Lover’s fiery finale, the “Karma” door on tour) was the perfect hue to bookend her last chapter and light the way into this one.
- What fans are predicting for Showgirl: potential collaborators, thematic shifts hinted by the briefcase’s mint-green lining, and whether we’ll see a full “Showgirl Tour” next year.
- How to watch her “New Heights” podcast episode (drops Aug. 13) for more hidden details, live reactions from the Kelce brothers and maybe even a surprise track snippet.
## What Is Gerrymandering?Imagine you and your friends want to split a big box of crayons so everyone gets to pick their favorite color. But one friend gets to draw the lines around each group of crayons in a tricky way so they end up with the most popular colors.Gerrymandering is when leaders draw the borders of voting areas (called districts) on a map so that one political party benefits more than another.---## How Does It Work?- A map is divided into districts where people vote for their leaders.
- If you squeeze or stretch a district to include more supporters of one party, that party wins more elections.
- Even if lots of people vote for the other party overall, the way the lines are drawn can make it look like they lost.---## Why Is It Unfair?- Some votes count more than others because of how the lines are drawn.
- Communities that usually vote the same way can get split up so they don’t have a strong voice.
- The party in charge stays in power even if more people voted for the other side.---## How Can We Stop Gerrymandering?- Have independent groups (not politicians) draw the districts.
- Use clear rules so districts stay connected and fair (for example, they can’t be super skinny or zig-zag).
- Let courts check the maps to make sure districts aren’t drawn in a sneaky way.---
# Maximizing HEPA Filter Benefits for Blood Pressure Control## 1. Choose the Right HEPA Purifier- Use a portable HEPA air purifier rated for your specific room size.
- Select models certified to remove fine particulate matter (PM₂.₅) with a high Clean Air Delivery Rate (CADR).---## 2. Optimal Placement and Continuous Operation1. Install one purifier in your bedroom and another in the living room—areas where you spend the most time.
2. Run units continuously, especially during peak traffic hours and at night, to maintain consistently low indoor PM levels.
3. Keep doors and windows closed whenever possible to minimize infiltration of outdoor particulates.---## 3. Regular Maintenance for Peak Performance- Replace HEPA filters according to manufacturer guidelines (usually every 6–12 months).
- Clean or vacuum pre-filters monthly to prevent dust buildup and airflow restriction.
- Watch for change indicators or increased noise (signs your filter is clogged).---## 4. Complementary Indoor Air Strategies- Seal gaps around windows and doors with weather stripping to block particle ingress.
- Eliminate indoor PM sources: no smoking, minimize candle burning, and avoid indoor grilling.
- Use an indoor air quality monitor to track PM₂.₅ levels and adjust purifier fan speeds accordingly.
- If available, integrate a balanced HVAC system with fresh-air intake and HEPA filtration.---## 5. Expected Impact on Blood PressureOne month of real HEPA filtration in homes near busy roads produced an average systolic blood pressure drop of 2.8 mm Hg in adults whose baseline SBP was ≥ 120 mm Hg. During sham filtration, SBP rose by 0.2 mm Hg—resulting in a net 3.0 mm Hg reduction attributable to HEPA use.---## 6. Beyond Air FiltrationWhile HEPA purifiers offer a meaningful 2–3 mm Hg systolic reduction, integrating lifestyle measures—regular exercise, dietary sodium reduction, and stress management—can further amplify cardiovascular benefits.---ReferencesHealio: “HEPA air filters may help improve blood pressure in people living near busy roads”
AirQualityNews: “High blood pressure? A simple air filter could help”
# Benefits of Creatine on the BrainCreatine is widely known for enhancing muscle performance, but it also plays a critical role in brain energy metabolism. By supporting the regeneration of ATP—the brain’s primary energy molecule—it helps neurons meet high energy demands, especially under stress or fatigue.## How Creatine Works in the BrainCreatine increases phosphocreatine stores in neural tissue, allowing rapid ATP recycling during periods of intense cognitive activity.
This mechanism helps maintain synaptic transmission, supports neuroplasticity, and guards against energy depletion during sleep loss or mental strain.## Key Cognitive Benefits- Improved memory performance compared to placebo, as demonstrated in a 2022 meta-analysis.
- Enhanced mental clarity and reduced cognitive fatigue during sleep deprivation scenarios.
- Potential mood stabilization and reduction of depressive symptoms in preliminary trials.
- Faster recovery of cognitive function following mild traumatic brain injury or concussion.## Neuroprotective and Clinical ImplicationsCreatine’s capacity to bolster neuronal energy reserves translates into neuroprotection. Early pilot studies indicate it may slow cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease and support recovery after head trauma, although larger clinical trials are still needed to confirm these effects.## Recommended Usage and ConsiderationsMost research on brain health uses a daily dose around 5 g of creatine monohydrate, mirroring athletic supplementation protocols.
In acute stress studies, single “megadoses” up to 35 g have shown cognitive benefits, but such high doses should be approached cautiously and under professional supervision.## Benefit Summary Table| Benefit | Target Group | Evidence |
|-------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------|----------------------------------------|
| Memory enhancement | General adults | Meta-analysis improvement |
| Cognitive performance under sleep deprivation | Sleep-deprived individuals | Single-dose German study |
| Neuroprotection after mild traumatic brain injury | Athletes, concussion patients | Emerging research on ATP support |
| Potential support in Alzheimer’s disease | Older adults, MCI patients | Pilot trial improvements |---## Next Steps and Emerging Research- Guanidinoacetic acid (GAA), a creatine precursor, may bypass rate-limiting synthesis steps and boost brain creatine even more efficiently.
- Vegetarians and vegans often have lower baseline creatine levels; they could see greater cognitive gains from supplementation.
- Ongoing trials are investigating whether long-term creatine use can alter the trajectory of neurodegenerative diseases.
# Darwin’s Bizarre Diet## Eating His DiscoveriesAccording to historical accounts, Darwin sampled at least one specimen of every new creature he discovered, turning scientific cataloging into a personal culinary challenge.---## The Cambridge “Glutton Club”While at Cambridge, he joined a gastronomic society devoted to consuming birds and beasts unfamiliar to the human palate.
The club’s weekly dinners featured hawks, herons, bitterns, and even a brown owl—whose “indescribable” flavor ultimately discouraged further owl-themed feasts.---## Culinary Adventures Aboard the BeagleDuring the HMS Beagle voyage, Darwin continued his edible experiments, dining on puma (which he likened to veal), iguanas, armadillos, and giant Galápagos tortoises.
He even sampled a cup of tortoise bladder fluid, describing it as “limpid” and “slightly bitter”.---## Favorite Exotic FareAmong his most memorable meals was an agouti—a 20-pound South American rodent he declared the “very best meat” he had ever tasted, highlighting his adventurous palate and willingness to eat what he studied.
# What Is a “Leftist”?A leftist is someone who wants to make sure everyone is treated fairly and kindly.They believe people should share what they have so that nobody feels left out or sad.## Things a Leftist Cares About
- Sharing toys, food, or money with people who need them
- Making rules so everyone gets a turn or a chance
- Helping people who are having a hard time## A Simple Example
Imagine you have ten cookies and your friend has none. A leftist would say, “Let’s share so we both have five.” That way, no one feels left out.
A Weck jar is a type of glass jar used primarily for home canning and preserving food. It originated in Germany and is known for its distinctive design and reusable components. Here's what makes a Weck jar special:### 🫙 Key Features:
- Glass Lid: Unlike Mason jars that use metal lids, Weck jars have a glass lid that sits on top of a rubber gasket.
- Rubber Gasket: This creates an airtight seal when the jar is processed in a water bath or pressure canner.
- Metal Clamps: Two small stainless steel clips hold the lid in place during processing. Once the jar cools and seals, the clips can be removed.
- Reusable: All parts (jar, lid, gasket, and clips) are reusable, making them eco-friendly.
- Stylish Design: Many people also use them for storage or decoration because of their clean, minimalist look.### Common Uses:
- Canning jams, jellies, pickles, and sauces
- Storing dry goods like grains, nuts, or spices
- Serving desserts or layered salads
- Decorative purposes (e.g., candles or flower vases)
"The most important aspect of love is not in giving or the receiving: it's in the being." Ram Dass
# Why Missouri Repealed Voter-Approved Paid Sick Leave---## Background: Proposition AOn November 5, 2024, Missouri voters approved Proposition A, which raised the state’s minimum wage and required most employers to provide earned paid sick leave—accrued at one hour for every 30 hours worked, up to 40 or 56 hours per year depending on employer size.---## Legislative Repeal: House Bill 567On July 10, 2025, Governor Mike Kehoe signed House Bill 567, passed by the legislature on June 30, 2025, which repealed the paid sick leave provisions of Proposition A. The repeal takes effect on August 28, 2025, effectively cancelling the people’s vote on that benefit.---## Reasons Cited for Repeal- The Missouri Chamber of Commerce and other business groups argued that mandatory paid sick leave was a “job killer” and imposed one-size-fits-all mandates that hurt economic competitiveness.
- Lawmakers described the sick-leave requirements as onerous record-keeping and cost burdens for small businesses, framing the repeal as rolling back government overreach.
- Governor Kehoe characterized the bill as protecting families, job creators, and small businesses by cutting taxes and eliminating costly mandates.---## What Happens NextWith the repeal set for August 28, 2025, employers in Missouri will no longer be required to offer the earned paid sick time mandated by voters. However, businesses may choose to continue offering paid leave voluntarily, and advocates are already preparing new ballot initiatives to reinstate these protections.
# TBR Meaning---## Primary Meaning in Reading ContextTBR stands for “To Be Read.” It refers to a list—physical, digital, or mental—of books that someone plans to read in the future.---## Other Common MeaningsAcross different fields, TBR can denote various phrases. Below is a snapshot of some widely recognized meanings:| Abbreviation | Meaning | Context |
|--------------|-----------------------------|-----------------------|
| TBR | Tennessee Board of Regents | Education/Government |
| TBR | To Be Reviewed | Writing/Publishing |
| TBR | To Be Returned | Logistics/Lending |
| TBR | Teenage Bottlerocket | Music/Band |---## Tips for Using TBR- In book communities, tagging a list or pile as your TBR helps organize reading plans.
- Platforms like Goodreads let you create a “To Be Read” shelf to track upcoming reads.
- Remember that TBR lists are flexible—feel free to shuffle, prune, or pause them to avoid feeling overwhelmed.---
# Managing Meniere’s Disease Without Medication## Dietary and Fluid BalanceAdopting a low-sodium diet and staying well hydrated can stabilize inner-ear fluid levels and reduce the frequency of vertigo episodes.- Aim for 1,500–2,000 mg of sodium per day by avoiding processed foods, canned goods, and high-salt snacks.
- Drink at least eight glasses of water daily; dehydration can worsen inner-ear fluid imbalances.
- Limit or avoid caffeine, alcohol, nicotine, and MSG, which may increase fluid retention and trigger attacks.---## Natural Supplements and RemediesCertain foods, herbs, and nutrients support nerve function, reduce inflammation, and may lessen symptoms.- Ginger eases vertigo-induced nausea through its anti-inflammatory and circulatory benefits.
- Magnesium-rich foods (spinach, almonds, bananas) support nerve and muscle health in the inner ear.
- Ensure adequate vitamin D via sunlight or diet (fatty fish, egg yolks) to support bone and nerve function.
- Herbal diuretics such as Ze Xie, Fu Ling, and Yi Yi Ren can gently promote fluid removal and reduce ear pressure.
- Peppermint, lavender, or ginger essential oils applied topically or diffused may help relieve dizziness, nausea, and stress.---## Physical Rehabilitation and ExerciseRetraining balance and movement can empower your brain to compensate for inner-ear dysfunction.- Vestibular Rehabilitation Therapy (VRT) uses tailored exercises to improve balance and reduce dizziness.
- Gentle yoga and tai chi enhance proprioception and promote relaxation, lowering stress-related triggers.---## Stress Management and Mental Well-BeingEmotional health plays a key role in symptom control and quality of life.- Practice mindfulness, deep breathing, or guided imagery daily to calm the nervous system and reduce attack triggers.
- Track symptoms in a diary to identify personal triggers and monitor progress.
- Consider joining a support group or working with a therapist to address anxiety, depression, and the stress of unpredictability.---By combining these lifestyle strategies, natural remedies, and rehabilitative techniques, many people with Meniere’s disease can significantly reduce or even prevent attacks—often without relying on daily medications. If you’d like to explore creating a personalized plan or learn more about specific exercises and herbal formulas, just let me know!
# Salty Food and Meniere’s Disease## How Salt Triggers Meniere’s AttacksExcess sodium makes your body retain extra fluid, and Meniere’s disease involves a buildup of fluid in the inner ear. When inner-ear pressure rises, it can precipitate vertigo, tinnitus, ear fullness, and hearing changes on the affected side---## Recommended Sodium Intake1. Aim for no more than 2,000 mg of sodium per day; some guidelines suggest an ideal limit closer to 1,500 mg daily.
2. Spreading sodium evenly across meals helps avoid sudden spikes in inner-ear fluid pressure that may trigger attacks---## Foods High in Sodium to Watch- Processed and cured meats (bacon, ham, salami)
- Canned foods and packaged mixes (soups, rice/pasta mixes)
- Pickled or brined items (olives, sauerkraut, pickles)
- Sauces and condiments (soy sauce, Worcestershire, bottled dressings)
- Snack foods (chips, salted nuts, crackers)---## Tips to Reduce Salt Intake- Cook with salt-free herbs, spices, or salt substitutes instead of table salt.
- Remove the salt shaker from your dining table.
- Read Nutrition Facts labels and choose “low-sodium” or “no-salt-added” versions.
- Favor fresh or frozen whole foods over canned or processed options.
- When dining out, request dishes to be prepared without added salt.---If you suspect salty foods are triggering your Meniere’s episodes, keep a food and symptom diary and discuss a tailored low-sodium plan with your healthcare provider.
# Symptoms of Meniere’s DiseaseMeniere’s disease is a chronic inner ear disorder characterized by unpredictable episodes of vertigo, fluctuating hearing loss, tinnitus, and aural fullness. During an episode, symptoms can last from 20 minutes up to 24 hours and may recur over time, sometimes progressing to permanent hearing impairment.## Main Symptoms- Vertigo: a spinning sensation that begins and stops suddenly, often accompanied by nausea and lasting between 20 minutes and 24 hours.
- Hearing loss: fluctuating initially—especially low-frequency sounds—and potentially permanent over time.
- Tinnitus: perception of ringing, buzzing, roaring, whistling, or hissing in the affected ear.
- Aural fullness: a feeling of pressure or fullness in one ear.## Additional and Associated Symptoms- Nausea and vomiting triggered by severe vertigo attacks.
- Drop attacks: sudden falls without loss of consciousness (Tumarkin’s otolithic crises).
- Uncontrolled eye movements (nystagmus) during episodes of vertigo.
- Cold sweats and paleness during acute dizziness.
- Gastrointestinal issues such as diarrhea during or after intense vertigo.
- Headaches or migraine-like pain in some patients.
- Fatigue and difficulty concentrating between episodes.
- Mood changes, ranging from irritability to anxiety, related to the unpredictability of attacks.---## Next StepsIf you experience recurrent vertigo or other hallmark signs of Meniere’s disease, consider seeing an otolaryngologist (ENT). Diagnostic evaluations—including audiometry and vestibular testing—can confirm the condition and help tailor treatments.
# Ways to Alleviate Meniere’s SymptomsBelow are strategies—ranging from diet tweaks to therapies and safety tips—that many find helpful in reducing the frequency and severity of Meniere’s episodes.## Dietary and Lifestyle Adjustments- Follow a low-sodium diet (1–2 g salt/day) to reduce inner-ear fluid buildup
- Limit or avoid caffeine, alcohol, nicotine, MSG, and high-tyramine foods (e.g., smoked meats, pickles) to prevent worsening of symptoms
- Stay well-hydrated (aim for at least 8 glasses of water daily) to help maintain proper fluid balance
- Identify and avoid personal triggers such as sudden head movements, bright lights, strong odors, and weather changes (barometric shifts)
- Balance carbohydrates with protein to stabilize insulin and support inner-ear homeostasis---## Medical Management- Use diuretics as prescribed to decrease inner-ear fluid pressure and help control vertigo
- Keep emergency medications on hand (e.g., meclizine, diazepam, promethazine, ondansetron) for acute attacks
- Consider a Meniett device, which delivers low-pressure pulses to improve fluid exchange in the ear canal
- Discuss intratympanic injections (steroids or gentamicin) with your ENT for severe, refractory vertigo—note gentamicin may risk further hearing loss---## Natural Remedies & Supplements- Sip ginger tea or take ginger capsules to soothe vertigo-related nausea and improve circulation
- Eat magnesium-rich foods (leafy greens, nuts, seeds, bananas) or supplement to support nerve and muscle function in the inner ear
- Ensure adequate vitamin D from sunlight, fatty fish, fortified foods, or supplements to support bone, nerve, and inner-ear health
- Try essential oils—peppermint for dizziness, lavender for relaxation, ginger for nausea—via inhalation or gentle massage behind the ears---## Therapies and Devices- Engage in vestibular rehabilitation therapy (VRT) to retrain balance and reduce dizziness long-term
- Use acupressure wristbands or ginger lozenges during attacks to ease nausea
- Explore acupuncture or other integrative approaches (evidence varies)—always coordinate with your healthcare team---## Stress Management & Mental Health- Practice mindfulness techniques (meditation, deep breathing, yoga) to lower stress, a known trigger for Meniere’s attacks
- Keep a symptom diary to pinpoint patterns and better avoid or prepare for episodes
- Seek counseling or join a support group to address anxiety, depression, and the emotional toll of chronic vertigo---## Practical Safety Measures- At the first sign of an attack, sit or lie down in a safe spot to prevent falls or injuries
- Carry a cane or walker if sudden vertigo poses a risk when standing or walking
- Inform family, friends, and coworkers about your condition so they can assist you during an attack---Working closely with your ENT, audiologist, and therapists will help tailor these strategies to your unique triggers and needs.
## What Is Universal Basic Income?Imagine every month you get a small allowance of money—no tests, no chores, no questions asked. Universal Basic Income (UBI) is like that for grown-ups. Everyone gets a little bit of money regularly so they can buy food, pay for a warm home, or have extra for fun things.## How Does It Help?When you know you’ll always get that money “cookie,” you feel safer. You won’t worry about running out of snacks or having no pillow to sleep on. It gives everyone a gentle boost so they can learn, work on new ideas, or take care of their families without being scared.## Where Does the Money Come From?Think of a giant piggy bank for our whole town. Grown-ups and companies put small amounts of money into it whenever they earn money—this is called a tax. Then the government takes coins from that big piggy bank and gives each person their monthly allowance.## Why Not Just Let People Work?UBI doesn’t stop people from working. It’s like having a safety net. If someone gets sick, is learning something new at school, or can’t find a job right away, they still have some money to live on. Then, when they restart working or find a new job, they aren’t starting from zero.
# Can Hunger Raise Blood Pressure?When you skip meals or go for extended periods without food, several compensatory mechanisms can kick in, sometimes driving blood pressure up rather than down.## Stress-Hormone Surge- Prolonged hunger triggers the release of cortisol and adrenaline.
- These hormones constrict blood vessels and increase heart rate, both of which elevate blood pressure.## Dehydration and Electrolyte Imbalance- Not eating often coincides with under-hydration. When you’re low on fluids, blood volume drops and the body narrows vessels to maintain pressure.
- Electrolyte shifts—especially low potassium—reduce the ability of arteries to relax, further increasing vascular resistance.## Contrast with Postprandial Effects- Right after eating, many people actually experience a temporary drop in blood pressure (postprandial hypotension) as blood is shunted to digestion; hunger elicits almost the opposite response.---Bottom Line: Brief periods without food usually don’t cause major blood-pressure changes. But if you’re chronically undernourished, dehydrated, or prone to stress spikes, skipping meals can raise your blood pressure through hormonal and vascular mechanisms.
Cost per use measures how much you effectively pay each time you use an item or service. Instead of focusing on the upfront price tag, it breaks down the total cost by the number of times you’ll actually use it. This lets you see whether something is a smart investment or an occasional splurge.To calculate it, divide the total cost by your expected number of uses. For example, a $120 gym membership that you use 40 times in a year works out to $3 per workout. Similarly, a $50 cast-iron skillet you expect to use 100 times costs you $0.50 each time.This metric helps you compare options and prioritize spending. If one kitchen gadget costs $30 but you only plan to use it twice, that’s $15 per use—probably better to borrow or rent. Meanwhile, a $300 multi-tool you’ll use 200 times is just $1.50 per use, making it a worthwhile purchase.Keep in mind that estimating future use can be tricky. If you vastly overestimate, your cost-per-use figure will look artificially low. To improve accuracy, track actual usage, include maintenance or subscription fees, and revisit your calculations periodically. This ensures you stay aligned with your real habits and budget goals.
High fructose corn syrup (HFCS) and cane sugar both supply glucose and fructose, but in slightly different forms. Cane sugar is sucrose, a molecule made of one glucose and one fructose linked together. HFCS contains free glucose and fructose in a ratio (often about 55% fructose, 45% glucose), so it doesn’t need that initial split.When you eat cane sugar, your small intestine uses an enzyme called sucrase to break sucrose into separate glucose and fructose. With HFCS, there’s no sucrose bond to break—your body can absorb the free sugars right away. This means HFCS can enter your system a bit faster, though both end up as glucose and fructose molecules.Glucose travels from your gut into your bloodstream, triggering insulin release so muscles and other tissues take it up for energy or storage as glycogen. Fructose, on the other hand, is absorbed differently—via specific transporters—and goes almost directly to the liver. Because fructose doesn’t cause an insulin spike, it’s treated more like a raw ingredient the liver can turn into fat or other compounds.In the liver, fructose is rapidly converted into building blocks for fat and stored triglycerides, especially when you’ve eaten more calories than you burn. Glucose that isn’t immediately used for energy is stored as glycogen in your liver and muscles or turned into fat more slowly. Over time, a high intake of free fructose (from HFCS or too much added sugar) may contribute to fatty liver, higher triglycerides, and insulin resistance more readily than glucose alone. Both sugars add calories, but the extra fructose load from HFCS can put extra stress on your liver.
A comparison trap is the tendency to measure your worth, success, or happiness against others instead of against your own goals and values. Rooted in Leon Festinger’s social comparison theory, it’s an almost automatic process: when we see someone who seems “better off,” we instinctively gauge ourselves against them; when we see someone “worse off,” we may highlight our own advantages.While occasional comparison can inform self-improvement, falling into the comparison trap often backfires. It amplifies feelings of envy, insecurity, anxiety, and low self-esteem, especially in a social-media-driven world where everyone’s highlights reel is on display. Rather than inspiring growth, it usually leaves people feeling chronically inferior and dissatisfied.Comparisons can sometimes motivate us—upward comparisons may spark ambition, and downward comparisons can boost confidence. However, research shows both types more often fuel negative emotions like fear, shame, and sadness. Over time, this erodes genuine self-worth and corrodes mental health.Escaping the comparison trap involves conscious shifts: practice self-compassion, focus on personal progress by comparing present you to past you, cultivate gratitude for your own journey, and limit exposure to curated social feeds. By anchoring self-evaluation in your values and unique path, you reclaim joy and foster authentic growth.
Aluminum is added to some vaccines as an adjuvant, which means it helps your immune system notice the vaccine’s ingredients and mount a stronger defense. By acting like a beacon that recruits immune cells, aluminum adjuvants let vaccines work effectively with smaller amounts of antigen and fewer doses.Decades of research and safety monitoring show that the tiny quantities of aluminum in vaccines aren’t harmful for people with normal kidney function. The amount in each shot is similar to what babies get in a liter of infant formula, and most of it – about half – is flushed out by the kidneys within 24 hours, with the rest gradually eliminated. Large studies, including one following over 1.2 million children, found no link between vaccine aluminum and long-term health issues like asthma or neurodevelopmental disorders. Only individuals with severe kidney impairment need special caution, since they clear aluminum more slowly.
# Difference Between Isopropyl Rubbing Alcohol and Ethyl Rubbing AlcoholBelow is a breakdown of how isopropyl-based and ethyl-based rubbing alcohols differ across key properties and uses.---## Chemical Structure- Isopropyl alcohol (isopropanol) has the formula C₃H₇OH.
- Ethyl alcohol (ethanol) is C₂H₅OH.
- The extra carbon and two hydrogen atoms in isopropanol give it slightly different physical and antimicrobial traits than ethanol.---## Common Uses- Both serve as disinfectants, antiseptics, and solvents in medical, cosmetic, and household products.
- Typical rubbing-alcohol concentrations range from 60–90% active alcohol (the rest is water and minor additives) to optimize germ-killing efficacy.---## Antiseptic and Disinfectant Efficacy- Both alcohols denature proteins and disrupt lipid membranes in bacteria and many viruses.
- Optimal antimicrobial activity occurs at around 70% concentration; stronger (≥95%) solutions evaporate too quickly to penetrate germs, weaker (<60%) solutions lack sufficient alcohol contact time.---## Skin and Safety Considerations- Ethyl rubbing alcohol causes less skin damage and irritation on repeated use compared to isopropyl, making ethanol-based formulas gentler for frequent antiseptic application.
- Isopropyl evaporates faster, so it feels less tacky and is often chosen for cleaning electronics or surfaces where rapid drying is prized.---## Toxicity and Ingestion Risks- Ethanol (ethyl alcohol) is the same type used in alcoholic beverages and is safe in moderate consumption—but denatured rubbing forms often contain additives to prevent drinking.
- Isopropanol is toxic if ingested even in small amounts; as little as 100 mL can be lethal.
- Neither should be consumed; accidental ingestion demands urgent medical attention.---## Evaporation Rate and Residue- Isopropyl’s faster evaporation makes it ideal for applications requiring quick drying and minimal residue.
- Ethyl’s slightly slower evaporation (due to molecular differences) can leave a bit more moisture, which may aid extended contact on skin for disinfection.---## Quick Comparison Table| Property | Isopropyl Rubbing Alcohol | Ethyl Rubbing Alcohol |
|------------------------------|-------------------------------|------------------------------|
| Chemical formula | C₃H₇OH | C₂H₅OH |
| Optimal concentration | 60–90% | 60–90% |
| Antimicrobial effectiveness | Excellent at 70% | Excellent at 70% |
| Skin irritation | Higher potential | Lower potential |
| Evaporation speed | Faster | Slower |
| Consumable? | No (toxic) | Denatured form: no (additives); beverage form: yes |
| Lethal oral dose | ~100 mL | Much higher (beverage grade) |
Your "gut" feeling about someone may stem from hidden bias. An unconscious (or implicit) bias is when someone holds a stereotypical belief but doesn’t know it. That belief then affects how they treat people. An example of an unconscious bias is similarity bias. This is when people favor others they have a lot in common with.Next time you have a “gut” feeling, pause and think about it. What are the reasons behind why you think this way?
# Missouri Residents Mulberry Buying ProgramThe Missouri Department of Conservation (MDC) runs an early “seed buy” program each summer, purchasing ripe red mulberry (and wild plum) fruit from state residents. This initiative helps MDC secure native plant seeds for restoration and conservation projects while offering landowners extra income for fruit they’d otherwise let go to waste.---## How It Works- Participants harvest ripe red mulberry or wild plum fruit from their own trees.
- Before picking, residents can bring a few leaves to the MDC office to confirm species (to avoid white vs. red mulberry mix-ups).
- Fruit is weighed and purchased on a walk-in basis or by appointment.---## Rates and Dates| Fruit Type | Purchase Price | Season Start | Notes |
| -------------- | ----------------- | --------------- | ------------------------------------------ |
| Red Mulberry | $6.00 per pound | June 9, 2025 | Look for small trees in shaded, moist woods. |
| Wild Plum | $1.95 per pound | July 7, 2025 | Fruit must be fully colored (red/orange/yellow); no green fruit accepted. |---## Location & Contact- MDC Chillicothe Office
- Address: 1707 Missouri Boulevard, Chillicothe, MO 64601
- Hours: Monday–Friday, 8 am–5 pm (closed 12 pm–1 pm for lunch)
- Phone: 660-646-6122Bring your harvest on a walk-in basis or call ahead to schedule a drop-off appointment.
MDC expands its seed-buy offerings in the fall when additional species ripen.
## Other Missouri “Buy” and “Buyback” ProgramsBeyond the summer Red Mulberry and Wild Plum buy, Missouri conservation agencies and partners run several similar programs to source native seeds and combat invasives:---### 1. Fall Seed Buy (Acorns and Hickory Nuts)
• Typically runs October–November at regional MDC offices.
• Landowners bring in white and black oak acorns and various hickory nuts.
• Seed is paid by the pound and used for statewide reforestation and habitat projects.---### 2. Callery (Bradford) Pear Buyback
• Hosted by the Missouri Invasive Plant Council in partnership with Forest ReLeaf of Missouri, Forrest Keeling Nursery, and MDC.
• Homeowners cut and bring in invasive Bradford pear trees and receive one free native tree in exchange.
• Seasonal, statewide events (e.g., April 22, 2025 dates; registration required).---### 3. Local and Community Conservation Cost-Share Programs
• While not pure “buys,” MDC’s Community Conservation Cost-Share and Forestry Cost-Share programs reimburse communities and nonprofits for on‐the‐ground conservation practices (native plantings, invasive control, forest management).
• Funding is awarded on a first‐come, first‐served basis each July.---### Finding the Latest Offers
- Contact your nearest regional MDC office for current seed‐buy dates and rates.
- Watch the Missouri Invasive Plant Council (moinvasives.org) for buyback events targeting specific invaders.
- Sign up for MDC’s e-newsletter for announcements of new or expanded “buy” and cost-share opportunities.
# Cooperages: The Craft and Facilities Behind Wooden Barrels## DefinitionA cooperage is a workshop or facility where wooden casks, barrels, and kegs are crafted, assembled, and repaired.Artisans in these workshops are called coopers, and the process they practice is known as coopering.These vessels are typically made from oak to ensure a watertight seal and to impart desirable flavors when aging liquids like wine, beer, and spirits.---## History of CooperingThe craft of coopering dates back centuries, originating in Europe as an essential trade for storing and transporting goods.Early coopers honed their skills to produce “tight” barrels—containers so precisely fitted that they could hold liquids without leaks.Over time, coopering evolved into a fine art, with specialized techniques for different wood species, barrel shapes, and toasting or charring levels to influence flavor profiles.---## Cooperage Workshop Processes1. Wood Selection and Seasoning
- Coopers choose high-quality oak (French, American, Hungarian, etc.)
- Staves are air-dried or kiln-seasoned to reduce moisture and prevent warping2. Stave Shaping and Assembly
- Each stave is planed to precise dimensions
- Staves are arranged in a circular form, bound with temporary hoops3. Heating and Bending
- The assembled staves are steamed or heated over an open fire
- Heat makes the wood pliable, allowing coopers to bend staves into the classic barrel shape4. Hooping and Sealing
- Permanent metal hoops are driven over the staves to lock them in place
- End caps (heads) are fitted, and the barrel is tested for leaks5. Toasting/Charring (Spirits Cooperage)
- Interior is exposed to controlled flames to char or toast the wood
- This step develops flavor compounds critical for aging whiskeys and bourbons---## Cooperages Around the World- France and Burgundy: Renowned for wine barrel cooperages, focusing on varied toasting profiles to influence tannin release.
- Kentucky, USA: Home to major bourbon cooperages in Louisville, Lebanon, Benton, and Morehead, producing charred oak barrels for aging whiskey.
- Illinois, USA: Crozehead Cooperage, one of only 26 U.S. cooperages, preserves hand-crafted barrel-making traditions in the Midwest.
- Australia and New Zealand: Emerging cooperage markets supporting local wine industries with both oak and alternative aging vessels.---## Modern Applications- Wine and Spirits Aging: Barrels remain the gold standard for developing complex aromas, mouthfeel, and color.
- Craft Distilleries and Breweries: Nano-cooperages supply small-batch producers seeking bespoke barrel profiles.
- Furniture and Décor: Retired barrels are repurposed into tables, planters, and lighting fixtures.
- Alternative Vessels: Some cooperages now offer amphorae, concrete eggs, and stainless-steel hybrids for experimental aging.---Whether rooted in centuries-old tradition or driving innovation in craft beverages, cooperages play a pivotal role in shaping the character and quality of many beloved liquids.
# What Does SSR Stand For?Below is a snapshot of some of the most common meanings of the acronym SSR across different fields.## Table of Common Meanings| Abbreviation | Meaning | Field | Citation |
|--------------|-------------------------------|---------------------|----------|
| SSR | Soviet Socialist Republic | Government/History | [1] |
| SSR | Server-Side Rendering | Web Development | [7] |
| SSR | Solid State Relay | Electronics | [7] |
| SSR | Secondary Surveillance Radar | Aviation/ATC | [7] |
| SSR | Simple Sequence Repeat | Molecular Biology | [7] |---## Detailed DescriptionsSoviet Socialist Republic refers to any of the constituent republics of the former USSR. Each SSR had its own government structures but was ultimately under the authority of Moscow’s central leadership.Server-Side Rendering is a web-development technique in which HTML is generated on the server rather than in the browser. This can improve initial load times and SEO performance.A Solid State Relay is an electronic switching device that uses semiconductor components instead of moving parts. SSRs switch faster and more quietly than mechanical relays and have longer operational lifespans.Secondary Surveillance Radar systems interrogate aircraft transponders to obtain identity and altitude data. Unlike primary radar, SSR provides discrete digital responses from each airplane’s transponder.Simple Sequence Repeats (also called microsatellites) are short, tandemly repeated DNA motifs. SSR markers are widely used in genetics for mapping, population studies, and forensic identification.---## Other Noteworthy Uses- Sustained Silent Reading (education)
- Self-Service Restaurant (hospitality)
- Sum of Squares due to Regression (statistics)
- Special Security Representative (diplomacy)SSR is a highly context-dependent acronym.
# Why Cupping Your Hand Changes How You SoundWhen you cup your hand over a headset microphone, you’re unintentionally reshaping its frequency response. Sound waves bounce between your hand and the mic grille, creating resonant peaks—especially in the low-mid frequencies around 1.8–2.2 kHz and again above 6 kHz. Those peaks emphasize warmth and presence, making voices seem richer and more intimate on the other end.---## How the Hand Creates an Acoustic CavityYour cupped hand forms a small enclosed space in front of the capsule, acting much like a Helmholtz resonator.
• It traps and reinforces certain bass and mid frequencies.
• It absorbs or blocks higher frequencies, smoothing out harsh “s” and “t” sounds.
The result feels like a built-in pop filter and bass boost all at once.---## Reduced Background Noise and PlosivesCupping also serves as a shield against room noise and breath blasts.
• Plosive consonants (“p,” “b”) lose their sudden air bursts.
• Ambient sounds from behind or the side are further attenuated.
By cutting high-frequency noise and plosive spikes, it can give a cleaner, more focused vocal pickup.---## Why It “Feels” BetterHumans often prefer voices with a pronounced mid-range “presence.”
When that warmth is boosted and harsh highs are tamed, speech feels clearer and more engaging—even if it’s technically a coloration of the original sound. That subtle color shift tricks our ears into thinking the mic is just “better.”---## The Trade-OffsWhile cupping might seem to improve clarity, it comes with downsides:
- You destroy the microphone’s designed pickup pattern, risking unpredictable tonal shifts and feedback in louder environments.
- It’s inconsistent—small changes in hand shape or position can radically alter what your listeners hear.
- You lose high-frequency detail and natural timbre, which some styles may miss.---To sum up, cupping your hand over a headset mic isn’t a secret pro technique—it’s an accidental filter that boosts mid and low-mid frequencies while damping highs and noise. The perceived improvement is simply your ears responding to a warmer, less brittle voice.
# Chinese Farmland Ownership in the U.S.A look at U.S. Department of Agriculture data shows Chinese‐linked entities hold a surprisingly small slice of American farmland overall—and none in the core Ozarks region.---## Nationwide SnapshotChinese companies affiliated with the Chinese Communist Party owned 346,915 acres of U.S. agricultural land as of the end of 2022, spread across 29 states.An updated USDA report for year-end 2023 puts Chinese‐linked holdings at about 276,000 acres, representing roughly 0.2% of all U.S. agricultural land.---## Distribution by State- Oregon: 198,000 acres
- Texas: 159,640 acres
- Maine: 98 acres
- The remaining acreage is scattered among 26 other states, mostly in the West and Plains.No significant tracts appear in Missouri or Arkansas outside those major clusters.---## Situation in the Ozarks- The Ozarks Plateau covers roughly 47,000 square miles (about 30 million acres) across southern Missouri and northern Arkansas.
- USDA data report zero acres owned by Chinese‐linked entities in counties that form the heart of the Ozarks.
- In practical terms, China owns 0% of the Ozarks region’s land—far below the national average of 0.2%.---## Takeaways and Further Questions- Despite headlines about foreign farmland purchases, Chinese holdings in the U.S. are heavily regionally skewed and minimal overall.
- If you’d like to explore how other nations compare, or how farmland ownership trends have shifted over the past decade, let me know!
Need to contact us? Email: itsmikefromwork[at]proton[dot]me